Reduced skin tumor development in cyclin D1-deficient mice highlights the oncogenic ras pathway in vivo
- PMID: 9716400
- PMCID: PMC317082
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.16.2469
Reduced skin tumor development in cyclin D1-deficient mice highlights the oncogenic ras pathway in vivo
Abstract
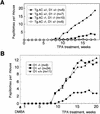
Cyclin D1 is part of a cell cycle control node consistently deregulated in most human cancers. However, studies with cyclin D1-null mice indicate that it is dispensable for normal mouse development as well as cell growth in culture. Here, we provide evidence that ras-mediated tumorigenesis depends on signaling pathways that act preferentially through cyclin D1. Cyclin D1 expression and the activity of its associated kinase are up-regulated in keratinocytes in response to oncogenic ras. Furthermore, cyclin D1 deficiency results in up to an 80% decrease in the development of squamous tumors generated through either grafting of retroviral ras-transduced keratinocytes, phorbol ester treatment of ras transgenic mice, or two-stage carcinogenesis.
Figures









References
-
- Aagaard L, Lukas J, Bartkova J, Kjerulff AA, Strauss M, Bartek J. Aberrations of p16Ink4 and retinoblastoma tumour-suppressor genes occur in distinct sub-sets of human cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1995;61:115–120. - PubMed
-
- Albanese C, Johnson J, Watanabe G, Eklund N, Vu D, Arnold A, Pestell RG. Transforming p21ras mutants and c-Ets-2 activate the cyclin D1 promoter through distinguishable regions. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:23589–23597. - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, Lukas J, Strauss M, Bartek J. The PRAD-1/cyclin D1 oncogene product accumulates aberrantly in a subset of colorectal carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1994;58:568–573. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi AB, Fischer SM, Robles AI, Rinchik EM, Conti CJ. Overexpression of cyclin D1 in mouse skin carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 1993;8:1127–1133. - PubMed
-
- Dlugosz AA, Cheng C, Denning MF, Dempsey PJ, Coffey RJ, Jr, Yuspa SH. Keratinocyte growth factor-receptor ligands induce TGFα expression and activate the epidermal growth factor-receptor signaling pathway in cultured epidermal keratinocytes. Cell Growth & Differ. 1994;5:1283–1292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
