Role of endogenous neurotensin in the behavioral and neuroendocrine effects of cocaine
- PMID: 9718595
- PMCID: PMC2386869
- DOI: 10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00028-1
Role of endogenous neurotensin in the behavioral and neuroendocrine effects of cocaine
Abstract
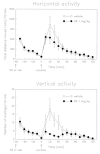
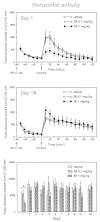
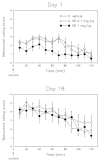
The present experiments were designed to assess the role of endogenous neurotensin (NT) in the behavioral response to acute and daily cocaine, after administration of the NT receptor antagonist, SR 48692. Given that glucocorticoids increase the sensitivity to the psychomotor effects of drugs of abuse, we also investigated the effects of SR 48692 on basal and cocaine-induced corticosterone secretion. Acute administration of SR 48692 (1 mg/kg i.p.) reduced the number of rearings induced by cocaine (15 mg/kg i.p.), without modifying horizontal activity. Repeated pretreatment with SR 48692 (1 mg/kg x 5 days) markedly reduced locomotion and rearings after an acute cocaine challenge (day 1), whereas the lower dose of SR 48692 (0.1 mg/kg) had no effect. SR 48692 (1 mg/kg), given daily before cocaine, also decreased cocaine-induced rearing on day 2, but had no effect on the following drug challenges (days 3-10). One week after discontinuing repeated cocaine injections, SR 48692 blocked vertical, but not horizontal, activity induced by an acute cocaine challenge. Rats treated repeatedly with cocaine showed an enhanced behavioral response characterized by the development of stereotypes, which were unaffected by SR 48692. Finally, treatment with SR 48692 did not alter corticosterone circadian secretion nor cocaine-stimulated corticosterone levels, indicating that the attenuation of the behavioral effects of cocaine after NT receptor blockade is not associated with blunted glucocorticoid secretion. These results indicate that administration of SR 48692 attenuates the locomotion and rearing response to cocaine but fails to modify stereotyped behavior, suggesting that SR 48692 modulates the behavioral effects of psychostimulant drugs by acting selectively on the mesolimbic dopaminergic system.
Figures


References
-
- Azzi M, Betancur C, Sillaber I, Spanagel R, Rostène W, Bérod A. Repeated administration of the neurotensin receptor antagonist SR 48692 differentially regulates mesocortical and mesolimbic dopaminergic systems. J Neurochem. in press. - PubMed
-
- Baumann MH, Rothman RB. Effects of acute and chronic cocaine on the activity of tuberoinfundibular dopamine neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 1993;608:175–179. - PubMed
-
- Betancur C, Rostène W, Bérod A. Chronic cocaine increases neurotensin gene expression in the shell of the nucleus accumbens and in discrete regions of the striatum. Mol Brain Res. 1997;44:334–340. - PubMed
-
- Blaha CD, Coury A, Fibiger HC, Phillips AG. Effects of neurotensin on dopamine release and metabolism in the rat striatum and nucleus accumbens: Cross-validation using in vivo voltammetry and microdialysis. Neuroscience. 1990;34:699–705. - PubMed
-
- Bordi F, Meller E. Enhanced stereotypies elicited by intrastriatal injection of D1 and D2 dopamine agonists in intact rats. Brain Res. 1989;504:276–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

