Mechanism of Cdc42-induced actin polymerization in neutrophil extracts
- PMID: 9722612
- PMCID: PMC2132886
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.4.1001
Mechanism of Cdc42-induced actin polymerization in neutrophil extracts
Abstract
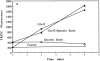
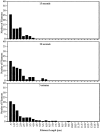
Cdc42, activated with GTPgammaS, induces actin polymerization in supernatants of lysed neutrophils. This polymerization, like that induced by agonists, requires elongation at filament barbed ends. To determine if creation of free barbed ends was sufficient to induce actin polymerization, free barbed ends in the form of spectrin-actin seeds or sheared F-actin filaments were added to cell supernatants. Neither induced polymerization. Furthermore, the presence of spectrin-actin seeds did not increase the rate of Cdc42-induced polymerization, suggesting that the presence of Cdc42 did not facilitate polymerization from spectrin-actin seeds such as might have been the case if Cdc42 inhibited capping or released G-actin from a sequestered pool. Electron microscopy revealed that Cdc42-induced filaments elongated rapidly, achieving a mean length greater than 1 micron in 15 s. The mean length of filaments formed from spectrin-actin seeds was <0.4 micron. Had spectrin-actin seeds elongated at comparable rates before they were capped, they would have induced longer filaments. There was little change in mean length of Cdc42-induced filaments between 15 s and 5 min, suggesting that the increase in F-actin over this time was due to an increase in filament number. These data suggest that Cdc42 induction of actin polymerization requires both creation of free barbed ends and facilitated elongation at these ends.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Cdc42-induced actin filaments are protected from capping protein.Curr Biol. 1999 Sep 9;9(17):979-82. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80428-x. Curr Biol. 1999. PMID: 10508585
-
Rho-family GTPases require the Arp2/3 complex to stimulate actin polymerization in Acanthamoeba extracts.Curr Biol. 1999 Apr 22;9(8):405-15. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80187-0. Curr Biol. 1999. PMID: 10226024
-
Regulation of actin polymerization in cell-free systems by GTPgammaS and Cdc42.J Cell Biol. 1997 Jul 28;138(2):363-74. doi: 10.1083/jcb.138.2.363. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9230078 Free PMC article.
-
Control of actin assembly at filament ends.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995;11:497-518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.11.110195.002433. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995. PMID: 8689567 Review.
-
Ras-related GTPases and the cytoskeleton.Mol Biol Cell. 1992 May;3(5):475-9. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.5.475. Mol Biol Cell. 1992. PMID: 1611153 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Arp2/3 complex mediates actin polymerization induced by the small GTP-binding protein Cdc42.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Dec 22;95(26):15362-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15362. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9860974 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of actin-associated proteins in smooth muscle contraction, cell proliferation, airway hyperresponsiveness and airway remodeling.Respir Res. 2015 Oct 30;16:134. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0296-1. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 26517982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Visualization and molecular analysis of actin assembly in living cells.J Cell Biol. 1998 Dec 28;143(7):1919-30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.7.1919. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9864364 Free PMC article.
-
ARF6 is required for growth factor- and rac-mediated membrane ruffling in macrophages at a stage distal to rac membrane targeting.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Dec;19(12):8158-68. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.12.8158. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10567541 Free PMC article.
-
A role for myosin-I in actin assembly through interactions with Vrp1p, Bee1p, and the Arp2/3 complex.J Cell Biol. 2000 Jan 24;148(2):353-62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.148.2.353. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10648568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen WE, Jones GE, Pollard JW, Ridley AJ. Rho, Rac and Cdc42 regulate actin organization and cell adhesion in macrophages. J Cell Sci. 1997;110:707–720. - PubMed
-
- Burbelo PD, Drechsel D, Hall A. A conserved binding motif defines numerous candidate target proteins for both Cdc42 and Rac GTPases. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:29071–29074. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

