Ribonuclease A variants with potent cytotoxic activity
- PMID: 9724716
- PMCID: PMC27907
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.18.10407
Ribonuclease A variants with potent cytotoxic activity
Abstract
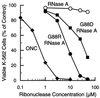
Select members of the bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A (RNase A) superfamily are potent cytotoxins. These cytotoxic ribonucleases enter the cytosol, where they degrade cellular RNA and cause cell death. Ribonuclease inhibitor (RI), a cytosolic protein, binds to members of the RNase A superfamily with inhibition constants that span 10 orders of magnitude. Here, we show that the affinity of a ribonuclease for RI plays an integral role in defining the potency of a cytotoxic ribonuclease. RNase A is not cytotoxic and binds RI with high affinity. Onconase, a cytotoxic RNase A homolog, binds RI with low affinity. To disrupt the RI-RNase A interaction, three RNase A residues (Asp-38, Gly-88, and Ala-109) that form multiple contacts with RI were replaced with arginine. Replacing Asp-38 and Ala-109 with an arginine residue has no effect on the RI-RNase interaction. In addition, these variants are not cytotoxic. In contrast, replacing Gly-88 with an arginine residue yields a ribonuclease (G88R RNase A) that retains catalytic activity in the presence of RI and is cytotoxic to a transformed cell line. Replacing Gly-88 with aspartate also yields a ribonuclease (G88D RNase A) with a decreased affinity for RI and cytotoxic activity. The cytotoxic potency of onconase, G88R RNase A, and G88D RNase A correlate with RI evasion. We conclude that ribonucleases that retain catalytic activity in the presence of RI are cytotoxins. This finding portends the development of a class of chemotherapeutic agents based on pancreatic ribonucleases.
Figures


References
-
- Raines R T. Chem Rev. 1998;98:1045–1065. - PubMed
-
- Riordan J F. In: Ribonucleases: Structures and Functions. D’Alessio G, Riordan J F, editors. New York: Academic; 1997. pp. 445–489.
-
- D’Alessio G, Di Donato A, Mazzarella L, Piccoli R. In: Ribonucleases: Structures and Functions. D’Alessio G, Riordan J F, editors. New York: Academic; 1997. pp. 383–423.
-
- Youle R J, D’Alessio G. In: Ribonucleases: Structures and Functions. D’Alessio G, Riordan J F, editors. New York: Academic; 1997. pp. 491–514.
-
- Suzuki H, Parente A, Farina B, Greco L, La Montagna R, Leone E. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987;368:1305–1312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

