FokI dimerization is required for DNA cleavage
- PMID: 9724744
- PMCID: PMC27935
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.18.10570
FokI dimerization is required for DNA cleavage
Abstract
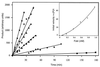
FokI is a type IIs restriction endonuclease comprised of a DNA recognition domain and a catalytic domain. The structural similarity of the FokI catalytic domain to the type II restriction endonuclease BamHI monomer suggested that the FokI catalytic domains may dimerize. In addition, the FokI structure, presented in an accompanying paper in this issue of Proceedings, reveals a dimerization interface between catalytic domains. We provide evidence here that FokI catalytic domain must dimerize for DNA cleavage to occur. First, we show that the rate of DNA cleavage catalyzed by various concentrations of FokI are not directly proportional to the protein concentration, suggesting a cooperative effect for DNA cleavage. Second, we constructed a FokI variant, FokN13Y, which is unable to bind the FokI recognition sequence but when mixed with wild-type FokI increases the rate of DNA cleavage. Additionally, the FokI catalytic domain that lacks the DNA binding domain was shown to increase the rate of wild-type FokI cleavage of DNA. We also constructed an FokI variant, FokD483A, R487A, which should be defective for dimerization because the altered residues reside at the putative dimerization interface. Consistent with the FokI dimerization model, the variant FokD483A, R487A revealed greatly impaired DNA cleavage. Based on our work and previous reports, we discuss a pathway of DNA binding, dimerization, and cleavage by FokI endonuclease.
Figures



References
-
- Sugisaki H, Kanazawa S. Gene. 1981;16:73–78. - PubMed
-
- Looney M, Moran L S, Jack W E, Feehery G R, Benner J S, Slatko B E, Wilson G G. Gene. 1989;80:193–208. - PubMed
-
- Kita K, Kotani H, Sugisaki H, Takanami M. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:5751–5756. - PubMed
-
- Kaczorowski T, Skowron P, Podhajska A J. Gene. 1989;80:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Skowron P, Kaczorowski T, Tucholski J, Podhajska A. Gene. 1993;125:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

