Characterization of a calmodulin kinase II inhibitor protein in brain
- PMID: 9724800
- PMCID: PMC27991
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.18.10890
Characterization of a calmodulin kinase II inhibitor protein in brain
Abstract
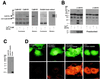
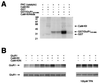
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaM-KII) regulates numerous physiological functions, including neuronal synaptic plasticity through the phosphorylation of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid-type glutamate receptors. To identify proteins that may interact with and modulate CaM-KII function, a yeast two-hybrid screen was performed by using a rat brain cDNA library. This screen identified a unique clone of 1.4 kb, which encoded a 79-aa brain-specific protein that bound the catalytic domain of CaM-KII alpha and beta and potently inhibited kinase activity with an IC50 of 50 nM. The inhibitory protein (CaM-KIIN), and a 28-residue peptide derived from it (CaM-KIINtide), was highly selective for inhibition of CaM-KII with little effect on CaM-KI, CaM-KIV, CaM-KK, protein kinase A, or protein kinase C. CaM-KIIN interacted only with activated CaM-KII (i. e., in the presence of Ca2+/CaM or after autophosphorylation) by using glutathione S-transferase/CaM-KIIN precipitations as well as coimmunoprecipitations from rat brain extracts or from HEK293 cells cotransfected with both constructs. Colocalization of CaM-KIIN with activated CaM-KII was demonstrated in COS-7 cells transfected with green fluorescent protein fused to CaM-KIIN. In COS-7 cells phosphorylation of transfected alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid-type glutamate receptors by CaM-KII, but not by protein kinase C, was blocked upon cotransfection with CaM-KIIN. These results characterize a potent and specific cellular inhibitor of CaM-KII that may have an important role in the physiological regulation of this key protein kinase.
Figures

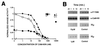
References
-
- Braun A P, Schulman H. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:417–445. - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Muller D, Derkach V, Griffith L C, Soderling T R. Science. 1997;276:2042–2045. - PubMed
-
- Pettit D L, Perlman S, Malinow R. Science. 1994;266:1881–1885. - PubMed
-
- Soderling T R. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1996;1297:131–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

