An alpha-tubulin mutant destabilizes the heterodimer: phenotypic consequences and interactions with tubulin-binding proteins
- PMID: 9725898
- PMCID: PMC25501
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.9.9.2349
An alpha-tubulin mutant destabilizes the heterodimer: phenotypic consequences and interactions with tubulin-binding proteins
Abstract
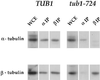
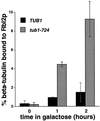
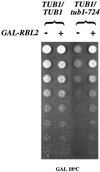
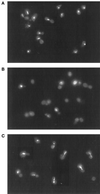
Many effectors of microtubule assembly in vitro enhance the polymerization of subunits. However, several Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes that affect cellular microtubule-dependent processes appear to act at other steps in assembly and to affect polymerization only indirectly. Here we use a mutant alpha-tubulin to probe cellular regulation of microtubule assembly. tub1-724 mutant cells arrest at low temperature with no assembled microtubules. The results of several assays reported here demonstrate that the heterodimer formed between Tub1-724p and beta-tubulin is less stable than wild-type heterodimer. The unstable heterodimer explains several conditional phenotypes conferred by the mutation. These include the lethality of tub1-724 haploid cells when the beta-tubulin-binding protein Rbl2p is either overexpressed or absent. It also explains why the TUB1/tub1-724 heterozygotes are cold sensitive for growth and why overexpression of Rbl2p rescues that conditional lethality. Both haploid and heterozygous tub1-724 cells are inviable when another microtubule effector, PAC2, is overexpressed. These effects are explained by the ability of Pac2p to bind alpha-tubulin, a complex we demonstrate directly. The results suggest that tubulin-binding proteins can participate in equilibria between the heterodimer and its components.
Figures



References
-
- Archer JE, Vega LR, Solomon F. Rbl2p, a yeast protein that binds to β-tubulin and participates in microtubule function in vivo. Cell. 1995;82:425–434. - PubMed
-
- Bond JF, Fridovich-Keil JL, Pillus L, Mulligan RC, Solomon F. A chicken-yeast chimeric β-tubulin protein is incorporated into mouse microtubules in vivo. Cell. 1986;44:461–468. - PubMed
-
- Caceres A, Kosik K. Inhibition of neurite polarity by tau antisense oligonucleotides in primary cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1990;343:461–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

