Binding of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-5 to smooth-muscle cell extracellular matrix is a major determinant of the cellular response to IGF-I
- PMID: 9725901
- PMCID: PMC25505
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.9.9.2383
Binding of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-5 to smooth-muscle cell extracellular matrix is a major determinant of the cellular response to IGF-I
Abstract
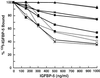
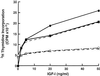
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5) has been shown to bind to fibroblast extracellular matrix (ECM). Extracellular matrix binding of IGFBP-5 leads to a decrease in its affinity for insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), which allows IGF-I to better equilibrate with IGF receptors. When the amount of IGFBP-5 that is bound to ECM is increased by exogenous addition, IGF-I's effect on fibroblast growth is enhanced. In this study we identified the specific basic residues in IGFBP-5 that mediate its binding to porcine smooth-muscle cell (pSMC) ECM. An IGFBP-5 mutant containing alterations of basic residues at positions 211, 214, 217, and 218 had the greatest reduction in ECM binding, although three other mutants, R214A, R207A/K211N, and K202A/R206N/R207A, also had major decreases. In contrast, three other mutants, R201A/K202N/R206N/R208A, and K217N/R218A and K211N, had only minimal reductions in ECM binding. This suggested that residues R207 and R214 were the most important for binding, whereas alterations in K211 and R218, which align near them, had minimal effects. To determine the effect of a reduction in ECM binding on the cellular replication response to IGF-I, pSMCs were transfected with the mutant cDNAs that encoded the forms of IGFBPs with the greatest changes in ECM binding. The ECM content of IGFBP-5 from cultures expressing the K211N, R214A, R217A/R218A, and K202A/R206N/R207A mutants was reduced by 79.6 and 71.7%, respectively, compared with cells expressing the wild-type protein. In contrast, abundance of the R201A/K202N/R206N/R208A mutant was reduced by only 14%. Cells expressing the two mutants with reduced ECM binding had decreased DNA synthesis responses to IGF-I, but the cells expressing the R201A/K202N/R206N/R208A mutant responded well to IGF-I. The findings suggest that specific basic amino acids at positions 207 and 214 mediate the binding of IGFBP-5 to pSMC/ECM. Smooth-muscle cells that constitutively express the mutants that bind weakly to ECM are less responsive to IGF-I, suggesting that ECM binding of IGFBP-5 is an important variable that determines cellular responsiveness.
Figures



References
-
- Arai A, Busby WH, Clemmons DR. Binding of insulin-like growth factor I or II to IGF binding protein 2 enables it to bind to heparin or extracellular matrix. Endocrinology. 1996a;137:4571–4575. - PubMed
-
- Arai T, Clarke J, Parker A, Busby WH, Clemmons DR. Effect of substitution of specific amino acids in insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 on heparin binding and its change in affinity for IGF-I in response to heparin. J Biol Chem. 1996b;271:6099–6106. - PubMed
-
- Borstein P, Sage EH. Thrombospondins. Methods Enzymol. 1994;245:62–85. - PubMed
-
- Camacho-Hubner C, Busby WH, McCusker RH, Wright G, Clemmons DR. Identification of the forms of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins produced by human fibroblasts and the mechanisms that regulate their secretion. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:11949–11956. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

