Human and yeast cdk-activating kinases (CAKs) display distinct substrate specificities
- PMID: 9725911
- PMCID: PMC25525
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.9.9.2545
Human and yeast cdk-activating kinases (CAKs) display distinct substrate specificities
Abstract
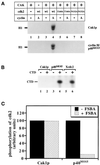
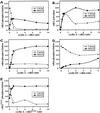
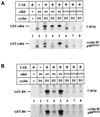
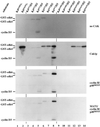
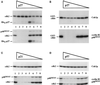
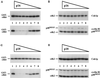
Cell cycle progression is controlled by the sequential functions of cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks). Cdk activation requires phosphorylation of a key residue (on sites equivalent to Thr-160 in human cdk2) carried out by the cdk-activating kinase (CAK). Human CAK has been identified as a p40(MO15)/cyclin H/MAT1 complex that also functions as part of transcription factor IIH (TFIIH) where it phosphorylates multiple transcriptional components including the C-terminal domain (CTD) of the large subunit of RNA polymerase II. In contrast, CAK from budding yeast consists of a single polypeptide (Cak1p), is not a component of TFIIH, and lacks CTD kinase activity. Here we report that Cak1p and p40(MO15) have strikingly different substrate specificities. Cak1p preferentially phosphorylated monomeric cdks, whereas p40(MO15) preferentially phosphorylated cdk/cyclin complexes. Furthermore, p40(MO15) only phosphorylated cdk6 bound to cyclin D3, whereas Cak1p recognized monomeric cdk6 and cdk6 bound to cyclin D1, D2, or D3. We also found that cdk inhibitors, including p21(CIP1), p27(KIP1), p57(KIP2), p16(INK4a), and p18(INK4c), could block phosphorylation by p40(MO15) but not phosphorylation by Cak1p. Our results demonstrate that although both Cak1p and p40(MO15) activate cdks by phosphorylating the same residue, the structural mechanisms underlying the enzyme-substrate recognition differ greatly. Structural and physiological implications of these findings will be discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Aprelikova O, Xiong Y, Liu ET. Both p16 and p21 families of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors block the phosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinases by the CDK-activating kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:18195–18197. - PubMed
-
- Blain SW, Montalvo E, Massagué J. Differential interaction of the cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk) inhibitor p27Kip1 with cyclin A-cdk2 and cyclin D2-cdk4. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:25863–25872. - PubMed
-
- Canagarajah BJ, Khokhlatchev A, Cobb MH, Goldsmith EJ. Activation mechanism of the MAP kinase ERK2 by dual phosphorylation. Cell. 1997;90:859–869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

