Use of highly encapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae strains in a flow-cytometric assay for assessment of the phagocytic capacity of serotype-specific antibodies
- PMID: 9729539
- PMCID: PMC95643
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.5.5.703-710.1998
Use of highly encapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae strains in a flow-cytometric assay for assessment of the phagocytic capacity of serotype-specific antibodies
Abstract
A phagocytosis assay for Streptococcus pneumoniae based on flow cytometry (FACS) with human polymorphonuclear cells and human complement was developed for the study of human vaccination antisera. Human prevaccination sera already contain high levels of C-polysaccharide (C-PS) antibodies, which are not protective in humans but which might give false positive results in a flow-cytometry-based assay. Cultures of S. pneumoniae grown to log phase on three consecutive days, followed by heat inactivation, yielded stable and highly encapsulated strains for serotypes 6A, 6B, 14, 19F, and 23F. As a result, only serotype-specific antibodies were able to facilitate phagocytosis of these strains, whereas no phagocytosis was observed with antibodies against C-PS or pneumococcal surface proteins. No, or weak, phagocytosis was observed with human prevaccination sera, whereas in general, postvaccination antisera facilitated phagocytosis. A highly significant correlation was observed between enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay titers and FACS phagocytosis titers (r = 0.98, P < 0.001) for serotype 23F pneumococci with human vaccination antisera. For all serotypes, interassay variation was below 10%. Major advantages of this assay over the classical killing assay are that (i) limited amounts of sera are required (10 microliter per titration curve), (ii) 600 samples can be processed in one day by one person, and (iii) cells can be fixed and measurement of the samples can be performed up to 1 week later.
Figures
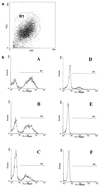

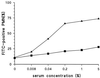
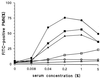

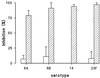
Comment in
-
Streptococcus pneumoniae flow-cytometric phagocytosis assay.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1999 May;6(3):444. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.6.3.444-444.1999. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10490330 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alonso de Velasco E, Verheul A F M, van Steijn A M P, Dekker H A T, Feldman R G, Fernández I M, Kamerling J P, Vliegenthart J F, Verhoef J, Snippe H. Epitope specificity of rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG) elicited by pneumococcal type 23F synthetic oligosaccharide- and native polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccines: comparison with human anti-polysaccharide 23F IgG. Infect Immun. 1994;62:799–808. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alonso De Velasco E, Dekker H A, Antal P, Jalink K P, van Strijp J A, Verheul A F M, Verhoef J, Snippe H. Adjuvant Quil A improves protection in mice and enhances opsonic capacity of antisera induced by pneumococcal polysaccharide conjugate vaccines. Vaccine. 1994;12:1419–1422. - PubMed
-
- Alonso De Velasco E, Dekker B A, Verheul A F M, Feldman R G, Verhoef J, Snippe H. Anti-polysaccharide immunoglobulin isotype levels and opsonic activity of antisera: relationships with protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection in mice. J Infect Dis. 1995;172:562–565. - PubMed
-
- Bardardottir E, Jonsson S, Jonsdottir I, Sigfusson A, Valdimarsson H. IgG subclass response and opsonization of Streptococcus pneumoniae after vaccination of healthy adults. J Infect Dis. 1990;162:482–488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

