Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins
- PMID: 9729609
- PMCID: PMC98934
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.62.3.775-806.1998
Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins
Abstract
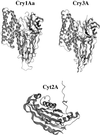
During the past decade the pesticidal bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis has been the subject of intensive research. These efforts have yielded considerable data about the complex relationships between the structure, mechanism of action, and genetics of the organism's pesticidal crystal proteins, and a coherent picture of these relationships is beginning to emerge. Other studies have focused on the ecological role of the B. thuringiensis crystal proteins, their performance in agricultural and other natural settings, and the evolution of resistance mechanisms in target pests. Armed with this knowledge base and with the tools of modern biotechnology, researchers are now reporting promising results in engineering more-useful toxins and formulations, in creating transgenic plants that express pesticidal activity, and in constructing integrated management strategies to insure that these products are utilized with maximum efficiency and benefit.
Figures






References
-
- Adams L F, Mathewes S, O’Hara P, Petersen A, Gürtler H. Elucidation of the mechanism of CryIIIA overproduction in a mutagenized strain of Bacillus thuringiensis var. tenebrionis. Mol Microbiol. 1994;14:381–389. - PubMed
-
- Adams L F, Thomas M D. Presented at the Seventh International Conference on Bacillus. Paris, France: Institut Pasteur; 1993.
-
- Adang M J, Brody M S, Cardineau G, Eagan N, Roush R T, Shewmaker C K, Jones A, Oakes J V, McBride K E. The reconstruction and expression of a Bacillus thuringiensis cryIIIA gene in protoplasts and potato plants. Plant Mol Biol. 1993;21:1131–1145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

