Efficient peripheral clonal elimination of B lymphocytes in MRL/lpr mice bearing autoantibody transgenes
- PMID: 9730892
- PMCID: PMC2213400
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.188.5.909
Efficient peripheral clonal elimination of B lymphocytes in MRL/lpr mice bearing autoantibody transgenes
Abstract
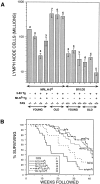
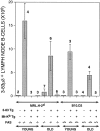
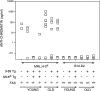
Peripheral B cell tolerance was studied in mice of the autoimmune-prone, Fas-deficient MRL/ lpr.H-2(d) genetic background by introducing a transgene that directs expression of membrane-bound H-2Kb antigen to liver and kidney (MT-Kb) and a second transgene encoding antibody reactive with this antigen (3-83mu delta, anti-Kk,b). Control immunoglobulin transgenic (Ig-Tg) MRL/lpr.H-2(d) mice lacking the Kb antigen had large numbers of splenic and lymph node B cells bearing the transgene-encoded specificity, whereas B cells of the double transgenic (Dbl-Tg) MRL/lpr.H-2(d) mice were deleted as efficiently as in Dbl-Tg mice of a nonautoimmune B10.D2 genetic background. In spite of the severely restricted peripheral B cell repertoire of the Ig-Tg MRL/lpr.H-2(d) mice, and notwithstanding deletion of the autospecific B cell population in the Dbl-Tg MRL/lpr.H-2(d) mice, both types of mice developed lymphoproliferation and exhibited elevated levels of IgG anti-chromatin autoantibodies. Interestingly, Dbl-Tg MRL/lpr.H-2(d) mice had a shorter lifespan than Ig-Tg MRL/lpr.H-2(d) mice, apparently as an indirect result of their relative B cell lymphopenia. These data suggest that in MRL/lpr mice peripheral B cell tolerance is not globally defective, but that certain B cells with receptors specific for nuclear antigens are regulated differently than are cells reactive to membrane autoantigens.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Analysis of central B cell tolerance in autoimmune-prone MRL/lpr mice bearing autoantibody transgenes.J Immunol. 1996 Jul 1;157(1):65-71. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8683157
-
Anti-Sm B cell differentiation in Ig transgenic MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice: altered differentiation and an accelerated response.J Immunol. 2001 Apr 15;166(8):5292-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.8.5292. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11290816
-
Autoreactive T cells revealed in the normal repertoire: escape from negative selection and peripheral tolerance.J Immunol. 2002 Apr 1;168(7):3188-94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.7.3188. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11907071
-
Self-reactive B cells in nonautoimmune and autoimmune mice.Immunol Res. 1998;17(1-2):49-61. doi: 10.1007/BF02786430. Immunol Res. 1998. PMID: 9479567 Review.
-
Unique site of IgG2a and rheumatoid factor production in MRL/lpr mice.Immunol Rev. 1997 Apr;156:103-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1997.tb00962.x. Immunol Rev. 1997. PMID: 9176703 Review.
Cited by
-
Contribution of alphabeta and gammadelta T cells to the generation of primary immunoglobulin G-driven autoimmune response in immunoglobulin- mu-deficient/lpr mice.Immunology. 2004 Jun;112(2):265-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01883.x. Immunology. 2004. PMID: 15147570 Free PMC article.
-
A fail-safe mechanism for negative selection of isotype-switched B cell precursors is regulated by the Fas/FasL pathway.J Exp Med. 2003 Nov 17;198(10):1609-19. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030357. J Exp Med. 2003. PMID: 14623914 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of IgG-switched autoreactive B cells and defects in Fas(lpr) lupus mice.J Immunol. 2010 Jul 15;185(2):1015-27. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000698. Epub 2010 Jun 16. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20554953 Free PMC article.
-
Activation and differentiation of autoreactive B-1 cells by interleukin 10 induce autoimmune hemolytic anemia in Fas-deficient antierythrocyte immunoglobulin transgenic mice.J Exp Med. 2002 Jul 1;196(1):141-6. doi: 10.1084/jem.20011519. J Exp Med. 2002. PMID: 12093879 Free PMC article.
-
Innate pathways to B-cell activation and tolerance.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Jan;1183:58-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05123.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20146708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Theofilopoulos AN, Dixon FJ. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:269–390. - PubMed
-
- Nagata S. Apoptosis by death factor. Cell. 1997;88:355–365. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Brannan CI, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Nagata S. Lymphoproliferation disorder in mice explained by defects in Fas antigen that mediates apoptosis. Nature. 1992;356:314–317. - PubMed
-
- Theofilopoulos AN, Kofler R, Singer PA, Dixon FJ. Molecular genetics of murine lupus models. Adv Immunol. 1989;46:61–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

