D-Ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase: cloning and heterologous expression of the spinach gene, and purification and characterization of the recombinant enzyme
- PMID: 9733539
- PMCID: PMC34857
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.118.1.199
D-Ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase: cloning and heterologous expression of the spinach gene, and purification and characterization of the recombinant enzyme
Abstract
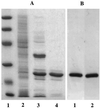
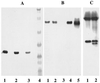
We have achieved, to our knowledge, the first high-level heterologous expression of the gene encoding D-ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase from any source, thereby permitting isolation and characterization of the epimerase as found in photosynthetic organisms. The extremely labile recombinant spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) enzyme was stabilized by DL-alpha-glycerophosphate or ethanol and destabilized by D-ribulose-5-phosphate or 2-mercaptoethanol. Despite this lability, the unprecedentedly high specific activity of the purified material indicates that the structural integrity of the enzyme is maintained throughout isolation. Ethylenediaminetetraacetate and divalent metal cations did not affect epimerase activity, thereby excluding a requirement for the latter in catalysis. As deduced from the sequence of the cloned spinach gene and the electrophoretic mobility under denaturing conditions of the purified recombinant enzyme, its 25-kD subunit size was about the same as that of the corresponding epimerases of yeast and mammals. However, in contrast to these other species, the recombinant spinach enzyme was octameric rather than dimeric, as assessed by gel filtration and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under nondenaturing conditions. Western-blot analyses with antibodies to the purified recombinant enzyme confirmed that the epimerase extracted from spinach leaves is also octameric.
Figures





References
-
- Anderson LE, Goldhaber-Gordon IM, Li D, Tang X, Xiang M, Prakash N. Enzyme-enzyme interaction in the chloroplast: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, triose phosphate isomerase and aldolase. Planta. 1995;196:245–255. - PubMed
-
- Bär J, Naumann M, Reuter R, Kopperschläger G. Improved purification of ribulose 5-phosphate 3-epimerase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and characterization of the enzyme. Bioseparation. 1996;6:233–241. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Buchanan BB. Regulation of the CO2 assimilation in oxygenic photosynthesis: the ferredoxin/thioredoxin system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991;288:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

