ADP-Glucose pyrophosphorylase from potato tubers. Site-directed mutagenesis studies of the regulatory sites
- PMID: 9733546
- PMCID: PMC34864
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.118.1.265
ADP-Glucose pyrophosphorylase from potato tubers. Site-directed mutagenesis studies of the regulatory sites
Abstract
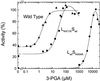
Several lysines (Lys) were determined to be involved in the regulation of the ADP-glucose (Glc) pyrophosphorylase from spinach leaf and the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 (K. Ball, J. Preiss [1994] J Biol Chem 269: 24706-24711; Y. Charng, A.A. Iglesias, J. Preiss [1994] J Biol Chem 269: 24107-24113). Site-directed mutagenesis was used to investigate the relative roles of the conserved Lys in the heterotetrameric enzyme from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tubers. Mutations to alanine of Lys-404 and Lys-441 on the small subunit decreased the apparent affinity for the activator, 3-phosphoglycerate, by 3090- and 54-fold, respectively. The apparent affinity for the inhibitor, phosphate, decreased greater than 400-fold. Mutation of Lys-441 to glutamic acid showed even larger effects. When Lys-417 and Lys-455 on the large subunit were mutated to alanine, the phosphate inhibition was not altered and the apparent affinity for the activator decreased only 9- and 3-fold, respectively. Mutations of these residues to glutamic acid only decreased the affinity for the activator 12- and 5-fold, respectively. No significant changes were observed on other kinetic constants for the substrates ADP-Glc, pyrophosphate, and Mg2+. These data indicate that Lys-404 and Lys-441 on the small subunit are more important for the regulation of the ADP-Glc pyrophosphorylase than their homologous residues in the large subunit.
Figures

References
-
- Ball K, Preiss J. Allosteric sites of the large subunit of the spinach leaf ADPglucose pyrophosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:24706–24711. - PubMed
-
- Charng Y, Iglesias AA, Preiss J. Structure-function relationships of cyanobacterial ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase: site-directed mutagenesis and chemical modification of the activator-binding sites of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase from Anabaena PCC 7120. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:24107–24113. - PubMed
-
- Fraser RDB, Suzuki E (1973) The use of least squares in data analysis. In SJ Leach, ed, Physical Principles and Techniques in Protein Chemistry, Part C. Academic Press, New York, pp 301–355
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

