Distinct biochemical and topological properties of the 31- and 27-kilodalton plasma membrane intrinsic protein subgroups from red beet
- PMID: 9733551
- PMCID: PMC34870
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.118.1.315
Distinct biochemical and topological properties of the 31- and 27-kilodalton plasma membrane intrinsic protein subgroups from red beet
Abstract
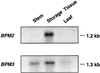
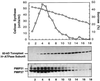
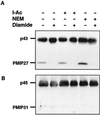
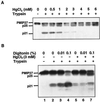
Plasma membrane vesicles from red beet (Beta vulgaris L.) storage tissue contain two prominent major intrinsic protein species of 31 and 27 kD (X. Qi, C.Y Tai, B.P. Wasserman [1995] Plant Physiol 108: 387-392). In this study affinity-purified antibodies were used to investigate their localization and biochemical properties. Both plasma membrane intrinsic protein (PMIP) subgroups partitioned identically in sucrose gradients; however, each exhibited distinct properties when probed for multimer formation, and by limited proteolysis. The tendency of each PMIP species to form disulfide-linked aggregates was studied by inclusion of various sulfhydryl agents during tissue homogenization and vesicle isolation. In the absence of dithiothreitol and sulfhydryl reagents, PMIP27 yielded a mixture of monomeric and aggregated species. In contrast, generation of a monomeric species of PMIP31 required the addition of dithiothreitol, iodoacetic acid, or N-ethylmaleimide. Mixed disulfide-linked heterodimers between the PMIP31 and PMIP27 subgroups were not detected. Based on vectorial proteolysis of right-side-out vesicles with trypsin and hydropathy analysis of the predicted amino acid sequence derived from the gene encoding PMIP27, a topological model for a PMIP27 was established. Two exposed tryptic cleavage sites were identified from proteolysis of PMIP27, and each was distinct from the single exposed site previously identified in surface loop C of a PMIP31. Although the PMIP31 and PMIP27 species both contain integral proteins that appear to occur within a single vesicle population, these results demonstrate that each PMIP subgroup responds differently to perturbations of the membrane.
Figures

References
-
- Agre P, Bonhivers M, Borgnia MJ. The aquaporins, blueprints for cellular plumbing systems. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:14659–14662. - PubMed
-
- Barone LM, Shih C, Wasserman BP. Mercury-induced conformational changes and identification of conserved surface loops in plasma membrane aquaporins from higher plants: topology of PMIP31 from Beta vulgarisL. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:30672–30677. - PubMed
-
- Barone LM, Wasserman BP. Generation and application of immunological probes for the study of membrane-bound proteins and enzymes: a review. J Food Biochem. 1996;20:173–192.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

