Mutational analysis of the transcriptional regulator GcvA: amino acids important for activation, repression, and DNA binding
- PMID: 9733689
- PMCID: PMC107511
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.18.4865-4871.1998
Mutational analysis of the transcriptional regulator GcvA: amino acids important for activation, repression, and DNA binding
Abstract
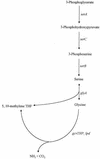
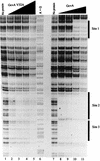
The GcvA protein is required for both glycine-mediated activation and purine-mediated repression of the gcvTHP operon. Random and site-directed PCR mutagenesis was used to create nucleotide changes in gcvA to identify residues of the protein involved in activation, repression, and DNA binding. Single amino acid substitutions at L30 and F31 cause a defect in activation of a gcvT-lacZ fusion but have no effect on repression or DNA binding. Single amino acid substitutions at V32 and S38 cause the loss of binding of GcvA to DNA. A deletion of the carboxy-terminal 14 amino acids of GcvA results in the loss of purine-mediated repression and, consequently, a constitutive activation of a gcvT-lacZ fusion. The results of this study partially define regions of GcvA involved in activation, repression, and DNA binding and demonstrate that these functions of GcvA are genetically separable.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

