Characterization of dacC, which encodes a new low-molecular-weight penicillin-binding protein in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 9733705
- PMCID: PMC107527
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.18.4967-4973.1998
Characterization of dacC, which encodes a new low-molecular-weight penicillin-binding protein in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
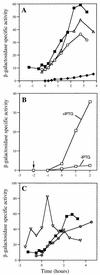
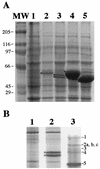
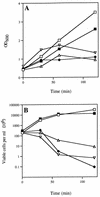
The pbp gene (renamed dacC), identified by the Bacillus subtilis genome sequencing project, encodes a putative 491-residue protein with sequence homology to low-molecular-weight penicillin-binding proteins. Use of a transcriptional dacC-lacZ fusion revealed that dacC expression (i) is initiated at the end of stationary phase; (ii) depends strongly on transcription factor sigmaH; and (iii) appears to be initiated from a promoter located immediately upstream of yoxA, a gene of unknown function located upstream of dacC on the B. subtilis chromosome. A B. subtilis dacC insertional mutant grew and sporulated identically to wild-type cells, and dacC and wild-type spores had the same heat resistance, cortex structure, and germination and outgrowth kinetics. Expression of dacC in Escherichia coli showed that this gene encodes an approximately 59-kDa membrane-associated penicillin-binding protein which is highly toxic when overexpressed.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

