Avian hepatitis B virus infection is initiated by the interaction of a distinct pre-S subdomain with the cellular receptor gp180
- PMID: 9733849
- PMCID: PMC110146
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.10.8089-8097.1998
Avian hepatitis B virus infection is initiated by the interaction of a distinct pre-S subdomain with the cellular receptor gp180
Abstract
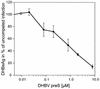
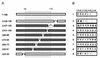
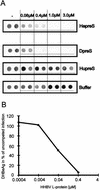
Functionally relevant hepadnavirus-cell surface interactions were investigated with the duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) animal model by using an in vitro infection competition assay. Recombinant DHBV pre-S polypeptides, produced in Escherichia coli, were shown to inhibit DHBV infection in a dose-dependent manner, indicating that monomeric pre-S chains were capable of interfering with virus-receptor interaction. Particle-associated pre-S was, however, 30-fold more active, suggesting that cooperative interactions enhance particle binding. An 85-amino-acid pre-S sequence, spanning about half of the DHBV pre-S chain, was characterized by deletion analysis as essential for maximal inhibition. Pre-S polypeptides from heron hepatitis B virus (HHBV) competed DHBV infection equally well despite a 50% difference in amino acid sequence and a much-reduced infectivity of HHBV for duck hepatocytes. These observations are taken to indicate (i) that the functionality of the DHBV pre-S subdomain, which interacts with the cellular receptor, is determined predominantly by a defined three-dimensional structure rather than by primary sequence elements; (ii) that cellular uptake of hepadnaviruses is a multistep process involving more than a single cellular receptor component; and (iii) that gp180, a cellular receptor candidate unable to discriminate between DHBV and HHBV, is a common component of the cellular receptor complex for avian hepadnaviruses.
Figures




References
-
- DeMeyer S, Gong J Z, Suwandhi W, van Pelt J, Soumillon A, Yap S H. Organ and species specificity of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection: a review of literature with a special reference to preferential attachment of HBV to human hepatocytes. J Viral Hepat. 1997;4:145–153. - PubMed
-
- Deng H, Liu R, Ellmeier W, Choe S, Unutmaz D, Burkhart M, Di M P, Marmon S, Sutton R E, Hill C M, Davis C B, Peiper S C, Schall T J, Littman D R, Landau N R. Identification of a major co-receptor for primary isolates of HIV-1. Nature. 1996;381:661–666. - PubMed
-
- Fehler, F., S. Seitz, and H. Schaller. Unpublished data.
-
- Feng Y, Broder C C, Kennedy P E, Berger E A. HIV-1 entry cofactor: functional cDNA cloning of a seven-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptor. Science. 1996;272:872–877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

