The reovirus protein mu2, encoded by the M1 gene, is an RNA-binding protein
- PMID: 9733883
- PMCID: PMC110211
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.10.8354-8357.1998
The reovirus protein mu2, encoded by the M1 gene, is an RNA-binding protein
Abstract
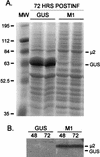
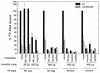
The reovirus M1, L1, and L2 genes encode proteins found at each vertex of the viral core and are likely to form a structural unit involved in RNA synthesis. Genetic analyses have implicated the M1 gene in viral RNA synthesis and core nucleoside triphosphatase activity, but there have been no direct biochemical studies of mu2 function. Here, we expressed mu2 in vitro and assessed its RNA-binding activity. The expressed mu2 binds both poly(I-C)- and poly(U)-Sepharose, and binding activity is greater in Mn2+ than in Mg2+. Heterologous RNA competes for mu2 binding to reovirus RNA transcripts as effectively as homologous reovirus RNA does, providing no evidence for sequence-specific RNA binding by mu2. Protein mu2 is now the sixth reovirus protein demonstrated to have RNA-binding activity.
Figures


References
-
- Brantley J D, Hunt A G. The N-terminal protein of the polyprotein encoded by potyvirus tobacco vein mottling virus is an RNA-binding protein. J Gen Virol. 1993;74:1157–1162. - PubMed
-
- Burd C G, Dreyfuss G. Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science. 1994;265:615–621. - PubMed
-
- Calnan B J, Tidor B, Biancalana S, Hudson D, Frankel A D. Arginine-mediated RNA recognition: the arginine fork. Science. 1991;252:1167–1171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

