Proviral structure, chromosomal location, and expression of HERV-K-T47D, a novel human endogenous retrovirus derived from T47D particles
- PMID: 9733890
- PMCID: PMC110222
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.10.8384-8391.1998
Proviral structure, chromosomal location, and expression of HERV-K-T47D, a novel human endogenous retrovirus derived from T47D particles
Abstract
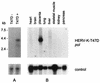
We previously described that type B retrovirus-like particles released from the human mammary carcinoma cell line T47D are pseudotypes and package retroviral RNA of different origins (W. Seifarth, H. Skladny, F. Krieg-Schneider, A. Reichert, R. Hehlmann, and C. Leib-Mösch, J. Virol. 69:6408-6416, 1995). One preferentially packaged retroviral sequence, ERV-MLN, has now been used to isolate the corresponding full-length provirus from a human genomic library. The 9,315-bp proviral genome comprises a complete retroviral structure except for a 3' long terminal repeat (LTR) truncation. A lysine tRNA primer-binding site and phylogenetic analyses assign this human endogenous retroviral element, now called HERV-K-T47D, to the HML-4 subgroup of the HERV-K superfamily. The gag, prt, pol, and env genes exhibit 40 to 60% amino acid identity to HERV-K10. HERV-K-T47D is located on human chromosome 10, with five closely related elements on chromosomes 8, 9, 15, 16, and 19 and several hundred HERV-K-T47D-related solitary LTRs dispersed over the human genome. HERV-K-T47D-related sequences are detected in the genomes of higher primates and Old World monkeys but not in those of New World monkeys. High HERV-K-T47D transcription levels were observed in human placenta tissue, whereas transcription in T47D cells was strictly steroid dependent.
Figures





Similar articles
-
HERV-IP-T47D, a novel type C-related human endogenous retroviral sequence derived from T47D particles.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 Mar 20;16(5):471-80. doi: 10.1089/088922200309133. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000. PMID: 10772533
-
Molecular biology of type A endogenous retrovirus.Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1990 Sep;63(2-3):77-90. Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1990. PMID: 1710682 Review.
-
Genome-wide screening, cloning, chromosomal assignment, and expression of full-length human endogenous retrovirus type K.J Virol. 1999 Nov;73(11):9187-95. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.11.9187-9195.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10516026 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and genomic organization of a novel human endogenous retrovirus family: HERV-K (HML-6).J Gen Virol. 1997 Jul;78 ( Pt 7):1731-44. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-78-7-1731. J Gen Virol. 1997. PMID: 9225050
-
HERV-K: the biologically most active human endogenous retrovirus family.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1996;13 Suppl 1:S261-7. doi: 10.1097/00042560-199600001-00039. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1996. PMID: 8797733 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of human endogenous retrovirus type K (HML-2) is activated by the Tat protein of HIV-1.J Virol. 2012 Aug;86(15):7790-805. doi: 10.1128/JVI.07215-11. Epub 2012 May 16. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22593154 Free PMC article.
-
HERV-K(HML-2), the Best Preserved Family of HERVs: Endogenization, Expression, and Implications in Health and Disease.Front Oncol. 2013 Sep 20;3:246. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00246. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24066280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of Human Endogenous Retrovirus Type K Envelope Protein is a Novel Candidate Prognostic Marker for Human Breast Cancer.Genes Cancer. 2011 Sep;2(9):914-22. doi: 10.1177/1947601911431841. Genes Cancer. 2011. PMID: 22593804 Free PMC article.
-
Variable transcriptional activity of endogenous retroviruses in human breast cancer.J Virol. 2008 Feb;82(4):1808-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02115-07. Epub 2007 Dec 12. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18077721 Free PMC article.
-
HERV-K(OLD): ancestor sequences of the human endogenous retrovirus family HERV-K(HML-2).J Virol. 2001 Oct;75(19):8917-26. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.19.8917-8926.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11533155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Sumidaie A M, Hart C A, Leinster S J, Green C D, McCarthy K. Particles with properties of retroviruses in monocytes from patients with breast cancer. Lancet. 1988;ii:5–9. - PubMed
-
- Boyd M T, Foley B, Brodsky I. Evidence for copurification of HERV-K-related transcripts and a reverse transcriptase activity in human platelets from patients with essential thrombocythemia. Blood. 1997;90:4022–4030. - PubMed
-
- Conrad B, Weissmahr R N, Böni J, Arcari R, Schüpbach J, Mach B. A human endogenous retroviral superantigen as candidate autoimmune gene in type I diabetes. Cell. 1997;90:303–313. - PubMed
-
- Cross S H, Charlton J A, Nan X, Bird A P. Purification of CpG islands using a methylated DNA binding column. Nat Genet. 1994;6:236–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

