Basic fibroblast growth factor is neither necessary nor sufficient for the development of retinal neovascularization
- PMID: 9736026
- PMCID: PMC1853023
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65619-2
Basic fibroblast growth factor is neither necessary nor sufficient for the development of retinal neovascularization
Abstract
Basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF2) is constitutively expressed in the retina and its expression is increased by a number of insults, but its role in the retina is still uncertain. This study was designed to test the hypothesis that altered expression of FGF2 in the retina affects the development of retinal neovascularization. Mice with targeted disruption of the Fgf2 gene had no detectable expression of FGF2 in the retina by Western blot, but retinal vessels were not different in appearance or total area from wild-type mice. When FGF2-deficient mice were compared with wild-type mice in a murine model of oxygen-induced ischemic retinopathy, they developed the same amount of retinal neovascularization. Transgenic mice with a rhodopsin promoter/Fgf2 gene fusion expressed high levels of FGF2 in retinal photoreceptors but developed no retinal neovascularization or other abnormalities of retinal vessels; in the ischemic retinopathy model, they showed no significant difference in the amount of retinal neovascularization compared with wild-type mice. These data indicate that FGF2 expression is not necessary nor sufficient for the development of retinal neovascularization. This suggests that agents that specifically antagonize FGF2 are not likely to be useful adjuncts in the treatment of retinal neovascularization and therapies designed to increase FGF2 expression are not likely to be complicated by retinal neovascularization.
Figures


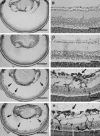
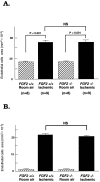

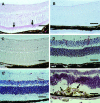
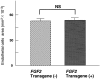
Comment in
-
Ocular neovascularization: clarifying complex interactions.Am J Pathol. 1998 Sep;153(3):665-70. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65607-6. Am J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9736014 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kahn H, Hiller R: Blindness caused by diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 1974, 78:58-67 - PubMed
-
- Michaelson I: The mode of development of the vascular system of the retina with some observations on its significance for certain retinal diseases. Trans Ophthalmol Soc UK 1948, 68:137-180
-
- Ashton N: Retinal vascularization in health and disease. Am J Ophthalmol 1957, 44:7-17 - PubMed
-
- Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E: Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature 1992, 359:843-845 - PubMed
-
- Plate KH, Breier G, Welch HA, Risau W: Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumor angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature 1992, 359:845-848 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

