Intracellular calcium and cell death during ischemia in neonatal rat white matter astrocytes in situ
- PMID: 9736645
- PMCID: PMC6793242
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-18-07232.1998
Intracellular calcium and cell death during ischemia in neonatal rat white matter astrocytes in situ
Abstract
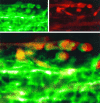
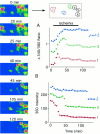
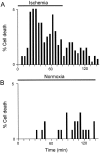
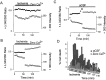
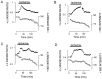
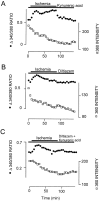
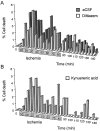
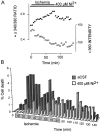
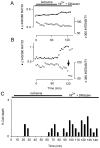
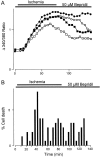
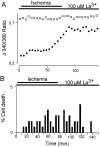
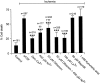
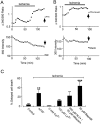
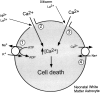
The major pathological correlate of cerebral palsy is ischemic injury of CNS white matter. Histological studies show early injury of glial cells and axons. To investigate glial cell injury, I monitored intracellular Ca2+ and cell viability in fura-2-loaded neonatal rat white matter glial cells during ischemia. Fura-2 fixation combined with immunohistochemistry revealed that fura-2-loaded cells were GFAP+/O4(-) and were therefore a population of neonatal white matter astrocytes. Significant ischemic Ca2+ influx was found, mediated by both L- and T-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Ca2+ influx via T-type channels was the most important factor during the initial stage of ischemia and was associated with significant cell death within 10-20 min of the onset of ischemia. The Na+-Ca2+ exchanger acted to remove cytoplasmic Ca2+ throughout the ischemic and recovery periods. Neither the release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores nor influx via glutamate-gated channels contributed to the rise in intracellular Ca2+ during ischemia. Ischemic cell death was reduced significantly by removing extracellular Ca2+ or by blocking voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. The exclusively voltage-gated Ca2+ channel nature of the Ca2+ influx, the role played by T-type Ca2+ channels, the protective effect of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger, and the lack of significant Ca2+ release from intracellular stores are features of ischemia that have not been reported in other CNS cell types.
Figures
References
-
- Banker BQ, Larroche J-C. Periventricular leukomalacia of infancy: a form of neonatal anoxic encephalopathy. Arch Neurol. 1962;7:386–410. - PubMed
-
- Barres BA, Koroshetz WJ, Chun LL, Corey DP. Ion channel expression by white matter glia: the type-1 astrocyte. Neuron. 1990;5:527–544. - PubMed
-
- Bevensee MO, Schwiening CJ, Boron WF. Use of BCECF and propidium iodide to assess membrane integrity of acutely isolated CA1 neurons from rat hippocampus. J Neurosci Methods. 1995;58:61–75. - PubMed
-
- Butt AM, Ransom BR. Morphology of astrocytes and oligodendrocytes during development in the intact rat optic nerve. J Comp Neurol. 1993;338:141–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
