Activity of the delta-opioid receptor is partially reduced, whereas activity of the kappa-receptor is maintained in mice lacking the mu-receptor
- PMID: 9736649
- PMCID: PMC6793240
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-18-07285.1998
Activity of the delta-opioid receptor is partially reduced, whereas activity of the kappa-receptor is maintained in mice lacking the mu-receptor
Abstract
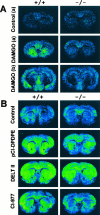
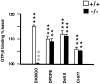
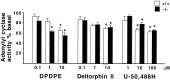
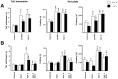
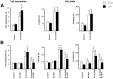
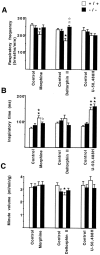
Previous pharmacological studies have indicated the possible existence of functional interactions between mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptors in the CNS. We have investigated this issue using a genetic approach. Here we describe in vitro and in vivo functional activity of delta- and kappa-opioid receptors in mice lacking the mu-opioid receptor (MOR). Measurements of agonist-induced [35S]GTPgammaS binding and adenylyl cyclase inhibition showed that functional coupling of delta- and kappa-receptors to G-proteins is preserved in the brain of mutant mice. In the mouse vas deferens bioassay, deltorphin II and cyclic[D-penicillamine2, D-penicillamine5] enkephalin exhibited similar potency to inhibit smooth muscle contraction in both wild-type and MOR -/- mice. delta-Analgesia induced by deltorphin II was slightly diminished in mutant mice, when the tail flick test was used. Deltorphin II strongly reduced the respiratory frequency in wild-type mice but not in MOR -/- mice. Analgesic and respiratory responses produced by the selective kappa-agonist U-50,488H were unchanged in MOR-deficient mice. In conclusion, the preservation of delta- and kappa-receptor signaling properties in mice lacking mu-receptors provides no evidence for opioid receptor cross-talk at the cellular level. Intact antinociceptive and respiratory responses to the kappa-agonist further suggest that the kappa-receptor mainly acts independently from the mu-receptor in vivo. Reduced delta-analgesia and the absence of delta-respiratory depression in MOR-deficient mice together indicate that functional interactions may take place between mu-receptors and central delta-receptors in specific neuronal pathways.
Figures
References
-
- Baamonde A, Dauge V, Ruiz-Gayo M, Fulga IG, Turcaud S, Fournie-Zaluski M-C, Roques BP. Antidepressant-type effects of endogenous enkephalins protected by systemic RB 101 are mediated by opioid δ and dopamine D1 receptor stimulation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992;216:157–166. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett D, Jr, Tenney SM. Control of breathing in experimental anemia. Respir Physiol. 1970;10:384–395. - PubMed
-
- Corbett AD, Paterson SJ, Kosterlitz HW. Selectivity of ligands for opioid receptors. In: Herz A, editor. Handbook of experimental pharmacology, Vol 104, Opioids I. Springer; New York: 1993. pp. 645–679.
-
- Cowan A, Zhu XZ, Mosberg HI, Omnaas JR, Porreca F. Direct dependence studies in rats with agents selective for different types of opioid receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988;246:950–955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
