Coatomer, Arf1p, and nucleotide are required to bud coat protein complex I-coated vesicles from large synthetic liposomes
- PMID: 9736713
- PMCID: PMC21619
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.19.11199
Coatomer, Arf1p, and nucleotide are required to bud coat protein complex I-coated vesicles from large synthetic liposomes
Abstract
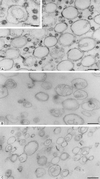
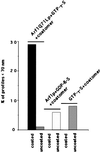
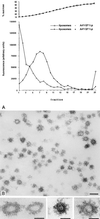
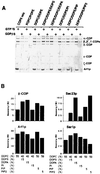
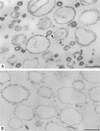
Synthetic coat protein complex I (COPI)-coated vesicles form spontaneously from large ( approximately 300 nm in diameter), chemically defined liposomes incubated with coatomer, Arf1p, and guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate. Coated vesicles are 40-70 nm in diameter, approximately the size of COPI vesicles formed from native membranes. The formation of COPI-coated buds and vesicles and the binding of Arf1p to donor liposomes depends on guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate. In contrast to the behavior of the COPII coat, coatomer binds to liposomes containing a variety of charged or neutral phospholipids. However, the formation of COPI buds and vesicles is stimulated by acidic phospholipids. In the absence of Arf1p, coatomer binds to liposomes containing dioleoylphosphatidic acid as a sole acidic phospholipid to form large coated surfaces without forming COPI-coated buds or vesicles. We conclude that Arf1p-GTP and coatomer comprise the minimum apparatus necessary to create a COPI-coated vesicle.
Figures
References
-
- Robinson M S. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994;6:538–644. - PubMed
-
- Bednarek S Y, Orci L, Schekman R. Trends Cell Biol. 1996;6:468–473. - PubMed
-
- Schekman R, Orci L. Science. 1996;271:1526–1533. - PubMed
-
- Bednarek S, Ravazzola M, Hosobuchi M, Amherdt M, Perrelet A, Schekman R, Orci L. Cell. 1995;83:1183–1196. - PubMed
-
- Orci L, Stamnes M, Ravazzola M, Amherdt M, Perrelet A, Söllner T H, Rothman J E. Cell. 1997;90:335–349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

