Human CUL-1 associates with the SKP1/SKP2 complex and regulates p21(CIP1/WAF1) and cyclin D proteins
- PMID: 9736735
- PMCID: PMC21641
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.19.11324
Human CUL-1 associates with the SKP1/SKP2 complex and regulates p21(CIP1/WAF1) and cyclin D proteins
Abstract
Deregulation of cell proliferation is a hallmark of cancer. In many transformed cells, the cyclin A/CDK2 complex that contains S-phase kinase associated proteins 1 and 2 (SKP1 and SKP2) is highly induced. To determine the roles of this complex in the cell cycle regulation and transformation, we have examined the composition of this complex. We report here that this complex contained an additional protein, human CUL-1, a member of the cullin/CDC53 family. The identification of CUL-1 as a member of the complex raises the possibility that the p19(SKP1)/p45(SKP2)/CUL-1 complex may function as the yeast SKP1-CDC53-F-box (SCF) protein complex that acts as a ubiquitin E3 ligase to regulate the G1/S transition. In mammalian cells, cyclin D, p21(CIP1/WAF1), and p27(KIP1) are short-lived proteins that are controlled by ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. To determine the potential in vivo targets of the p19(SKP1)/p45(SKP2)/CUL-1 complex, we have used the specific antisense oligodeoxynucleotides against either SKP1, SKP2, or CUL-1 RNA to inhibit their expression. Treatment of cells with these oligonucleotides caused the selective accumulation of p21 and cyclin D proteins. The protein level of p27 was not affected. These data suggest that the human p19(SKP1)/p45(SKP2)/CUL-1 complex is likely to function as an E3 ligase to selectively target cyclin D and p21 for the ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation. Aberrant expression of human p19(SKP1)/p45(SKP2)/CUL-1 complex thus may contribute to tumorigenesis by regulating the protein levels of G1 cell cycle regulators.
Figures
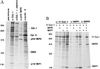

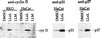
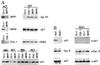
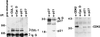

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

