A dominant role for non-MHC gene effects in susceptibility to cyclosporin A (CsA)-induced autoimmunity
- PMID: 9737659
- PMCID: PMC1905053
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00667.x
A dominant role for non-MHC gene effects in susceptibility to cyclosporin A (CsA)-induced autoimmunity
Abstract
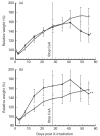
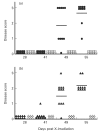
Lethally irradiated LEW rats reconstituted with syngeneic bone marrow and given CsA for a 4-week period develop a graft-versus-host-like disease upon withdrawal of CsA. This T cell-mediated autoimmune disease is referred to as CsA-induced autoimmunity (CsA-AI). CsA-AI-susceptible LEW rats and resistant BN rats differ greatly in the composition of their peripheral T cell compartment. To dissect the role of MHC and non-MHC genes in the development of peripheral T cell subsets in combination with susceptibility to CsA-AI the respective MHC congenic strains (LEW-1N and BN-1L) were examined for their T cell subsets and for their ability to develop CsA-AI. In this study we show that the Th1/Th2-like cell ratio as well as susceptibility to CsA-AI are under control of the non-MHC genes. This suggests that the Th1/Th2-like cell ratio is a critical determinant for development of CsA-AI. Alternatively, resistance can be attributed to lack of target organ susceptibility due to the absence of the target autoantigen in resistant rat strains. This interpretation is rejected, since both BN as well as BN-1L rats consistently develop the characteristic macroscopic and microscopic signs of CsA-AI upon adoptive transfer with autoreactive LEW-1N and LEW T cells, respectively. Therefore, it can be concluded that the non-MHC genes encode for immune deviation and thereby determine susceptibility or resistance to CsA-AI.
Figures

References
-
- Happ MP, Wettstein P, Dietzschold B, et al. Genetic control of the development of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats. Separation of MHC and non-MHC gene effects. J Immunol. 1988;141:1489–94. - PubMed
-
- Lorentzen JC, Klareskog L. Susceptibility of DA rats to arthritis induced with adjuvant oil or rat collagen is determined by genes both within and outside the major histocompatibility complex. Scand J Immunol. 1996;44:592–8. - PubMed
-
- Jones RS, Hess AD, Mann RB, et al. Induction of graft-versus-host disease after autologous bone marrow transplantation. Lancet. 1989;1:754–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

