Complement regulation in innate immunity and the acute-phase response: inhibition of mannan-binding lectin-initiated complement cytolysis by C-reactive protein (CRP)
- PMID: 9737662
- PMCID: PMC1905066
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00663.x
Complement regulation in innate immunity and the acute-phase response: inhibition of mannan-binding lectin-initiated complement cytolysis by C-reactive protein (CRP)
Abstract
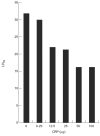
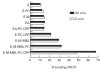
Mannan-binding lectin (MBL) is an acute-phase protein which activates complement at the level of C4 and C2. We recently reported that the alternative pathway also is required for haemolysis via this 'lectin pathway' in human serum. CRP is another acute-phase reactant which activates the classical pathway, but CRP also inhibits the alternative pathway on surfaces to which it binds. Since serum levels of both proteins generally increase with inflammation and tissue necrosis, it was of interest to determine the effect of CRP on cytolysis via the lectin pathway. We report here that although CRP increases binding of C4 to MBL-sensitized erythrocytes, which in turn enhances lectin pathway haemolysis, it inhibits MBL-initiated cytolysis by its ability to inhibit the alternative pathway. This inhibition is characterized by increased binding of complement control protein H and decreased binding of C3 and C5 to the indicator cells, which in turn is attributable to the presence of CRP. Immunodepletion of H leads to greatly enhanced cytolysis via the lectin pathway, and this cytolysis is no longer inhibited by CRP. These results indicate that CRP regulates MBL-initiated cytolysis on surfaces to which both proteins bind by modulating alternative pathway recruitment through H, pointing to CRP as a complement regulatory protein, and suggesting a co-ordinated role for these proteins in complement activation in innate immunity and the acute-phase response.
Figures
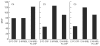
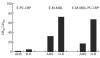
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of complement-dependent haemolysis via the lectin pathway: role of the complement regulatory proteins.Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Sep;117(3):442-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00998.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10469045 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of lectin pathway haemolysis by immunoglobulins.Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Sep;117(3):435-41. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00996.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10469044 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement for the alternative pathway as well as C4 and C2 in complement-dependent hemolysis via the lectin pathway.J Immunol. 1998 Mar 15;160(6):3006-13. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9510205
-
Lysis via the lectin pathway of complement activation: minireview and lectin pathway enhancement of endotoxin-initiated hemolysis.Immunopharmacology. 1999 May;42(1-3):81-90. doi: 10.1016/s0162-3109(99)00029-6. Immunopharmacology. 1999. PMID: 10408369 Review.
-
C-type lectins and galectins mediate innate and adaptive immune functions: their roles in the complement activation pathway.Dev Comp Immunol. 1999 Jun-Jul;23(4-5):401-20. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(99)00020-8. Dev Comp Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10426431 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the property of C-reactive protein to activate the classical pathway of complement in protecting mice from pneumococcal infection.J Immunol. 2006 Apr 1;176(7):4369-74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.7.4369. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16547275 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Serum Mannose-Binding Lectin Levels Are Associated with Poor Outcome After Acute Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Dec;52(3):1330-1340. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8941-0. Epub 2014 Oct 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25341475
-
Mechanism of complement-dependent haemolysis via the lectin pathway: role of the complement regulatory proteins.Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Sep;117(3):442-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00998.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10469045 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-independent haemolysis via the lectin pathway of complement activation in the guinea-pig and other species*.Immunology. 1999 Aug;97(4):686-92. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00810.x. Immunology. 1999. PMID: 10457224 Free PMC article.
-
An overview on human serum lectins.Heliyon. 2020 Aug 27;6(8):e04623. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04623. eCollection 2020 Aug. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32923708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Holmskov U, Malhotra R, Sim RB, et al. Collectins: collagenous C-type lectins of the innate immune system defense system. Immunol Today. 1994;15:67–74. - PubMed
-
- Epstein J, Eichbaum Q, Sheriff S, et al. The collectins in innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996;8:29–35. - PubMed
-
- Drickamer K, Taylor ME. Biology of animal lectins. Ann Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:237–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

