FcgammaRIa-gamma-chain complexes trigger antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) in CD5+ B cell/macrophage IIA1.6 cells
- PMID: 9737671
- PMCID: PMC1905059
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00666.x
FcgammaRIa-gamma-chain complexes trigger antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) in CD5+ B cell/macrophage IIA1.6 cells
Abstract
Most receptors for immunoglobulins exist as multi-subunit complexes, with unique ligand binding alpha-chains, combined with accessory signalling (gamma-, beta-, or zeta-) chains. The myeloid class I receptor for IgG (FcgammaRIa) has been shown to be dependent on the FcR gamma-chain for surface expression in vivo. In this study we assess the capacity of FcgammaRIa-gamma-chain complexes expressed in IIA1.6 cells to trigger phagocytosis and ADCC. An intact immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) signalling motif proved essential for triggering of biological function via the FcgammaRIa receptor complex. Both the FcR gamma-chain and the FcgammaRIIa-ITAM proved active in directing phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus and ADCC of erythrocytes, triggered by the FcgammaRIa complex. The capacity of FcgammaRIa to trigger phagocytic and cytolytic activity by IIA1.6 cells, both considered 'professional phagocyte' functions, motivated us to re-evaluate the cell lineage and developmental stage of IIA1.6 cells. Although originally described as mouse B lymphocytes, the IIA1.6 cells proved positive for non-specific esterase activity and expressed the CD5 antigen. These combined characteristics place the IIA1.6 cells within a unique CD5+ B cell/macrophage lineage, optimally suited for cell biological analyses of phagocyte receptors.
Figures
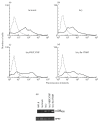
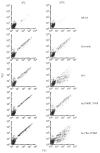
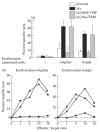

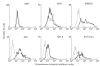
References
-
- Van de Winkel JGJ, Capel PJA. In: Human IgG Fc receptors. Austin Texas, Landes R.G., editors. 1996.
-
- Hibbs ML, Selvaraj P, Carpen O, Springer TA, Kuster H, Jouvin M-H, Kinet J-P. Mechanisms for regulating expression of membrane isoforms of FcγRIII (CD16) Science. 1989;246:1608–11. - PubMed
-
- Blank U, Ra C, Miller L, White K, Metger H, Kinet J-P. Complete structure and expression in transfected cells of high affinity IgE receptor. Nature. 1989;337:187–9. - PubMed
-
- Van Vugt MJ, Heijnen Iafm, Capel PJA, Park SY, Ra C, Saito T, Verbeek JS, Van de Winkel JGJ. FcR γ-chain is essential for both surface expression and function of human FcγRI (CD64) in vivo. Blood. 1996;87:3593–9. - PubMed
-
- Isashi Y, Yamashita T, Nagasawa S, Murakami M, Uede T. Molecular cloning and characterization of guinea pig FcγRIII: expression but not function is independent of the γ chain of FcɛRI. Int Immunol. 1996;8:1335–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

