Preferences for chemotherapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: descriptive study based on scripted interviews
- PMID: 9740561
- PMCID: PMC28665
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.317.7161.771
Preferences for chemotherapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: descriptive study based on scripted interviews
Abstract
Objective: To determine how patients with lung cancer value the trade off between the survival benefit of chemotherapy and its toxicities.
Design: Scripted interviews that included three hypothetical scenarios. Each scenario described the same patient with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with an expected survival of 4 months without treatment. Subjects were asked to indicate the minimum survival benefit required to accept the side effects of chemotherapy in the first two scenarios (mild toxicity and severe toxicity). In the third scenario, subjects were asked to choose between chemotherapy and supportive care when the benefit of chemotherapy was either to prolong life by 3 months or to palliate symptoms.
Subjects: 81 patients previously treated with cis-platinum based chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
Main outcome measure: Survival threshold for accepting chemotherapy.
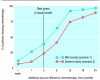
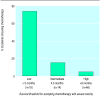
Results: The minimum survival threshold for accepting the toxicity of chemotherapy varied widely in patients. Several patients would accept chemotherapy for a survival benefit of 1 week, while others would not choose chemotherapy even for a survival benefit of 24 months. The median survival threshold for accepting chemotherapy was 4.5 months for mild toxicity and 9 months for severe toxicity. When given the choice between supportive care and chemotherapy only 18 (22%) patients chose chemotherapy for a survival benefit of 3 months; 55 (68%) patients chose chemotherapy if it substantially reduced symptoms without prolonging life.
Conclusions: Patients' willingness to accept chemotherapy for the treatment of metastatic lung cancer varies widely. Many would not choose chemotherapy for its likely survival benefit of 3 months but would if it improved quality of life. The conflict between these patients' preferences and the care they previously received has several explanations, one being that some patients had not received the treatment they would have chosen had they been fully informed.
Figures
Comment in
-
Managing patients with lung cancer. Effective communication, palliative care, and guidelines are needed.BMJ. 2000 Feb 5;320(7231):379; author reply 380. BMJ. 2000. PMID: 10657345 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Parker S, Tong T, Bolden S, Wingo P. Cancer statistics, 1997. CA Cancer J Clin. 1997;47:5–27. - PubMed
-
- Ginsberg R, Kris M, Armstrong J. Cancer of the lung: non-small cell lung cancer. In: DeVita JV, Hellman S, Rosenberg S, editors. Cancer: principles and practice of oncology. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 1993. pp. 673–723.
-
- Grilli R, Oxman A, Julian J. Chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: how much benefit is enough? J Clin Oncol. 1993;11:1866–1872. - PubMed
-
- Marino P, Pampallona S, Preatoni A, Cantoni A, Invernizzi F. Chemotherapy vs supportive care in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: results of a meta-analysis of the literature. Chest. 1994;106:861–865. - PubMed
-
- Souquet PJ, Chauvin F, Boissel JP, Cellerino R, Cormier Y, Ganz PA, et al. Polychemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 1993;342:19–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
