Coactivator TIF1beta interacts with transcription factor C/EBPbeta and glucocorticoid receptor to induce alpha1-acid glycoprotein gene expression
- PMID: 9742105
- PMCID: PMC109174
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.10.5880
Coactivator TIF1beta interacts with transcription factor C/EBPbeta and glucocorticoid receptor to induce alpha1-acid glycoprotein gene expression
Abstract
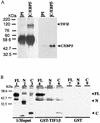
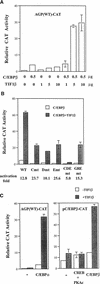
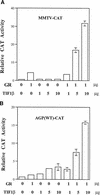
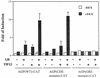
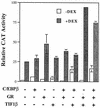
The transcription of the alpha1-acid glycoprotein gene is induced by inflammatory cytokines and glucocorticoids. C/EBPbeta is a major transcription factor involved in the induction of the agp gene by some cytokines. In this report, we have identified a novel transcriptional intermediary factor, TIF1beta, which could enhance the transcription of the agp gene by the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and C/EBPbeta. TIF1beta belongs to a subgroup of RING (really interesting new gene) finger proteins that contain a RING finger preceding two B box-type fingers and a putative coiled-coil domain (RBCC domain). Immunoprecipitation experiments showed that the interaction between GR and TIF1beta is ligand independent. The overexpression of the TIF1beta gene enhances GR-regulated expression in a ligand- and glucocorticoid-responsive element (GRE)-dependent manner. TIF1beta can also augment C/EBPbeta-mediated activity on wild-type and GRE-mutated agp genes, but this augmentation is diminished when all three C/EBPbeta-binding elements are mutated. Functional and biochemical characterizations indicated that the bZIP domain of C/EBPbeta and the RBCC domain, plant homeodomain finger, and bromodomain of TIF1beta are crucial for the interactions of these proteins. Taken together, these results suggest that TIF1beta serves as a converging mediator of signal transduction pathways of glucocorticoids and some inflammatory cytokines.
Figures

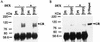
Similar articles
-
TIF1beta/KAP-1 is a coactivator of the orphan nuclear receptor NGFI-B/Nur77.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 22;284(21):14147-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809023200. Epub 2009 Mar 25. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19321449 Free PMC article.
-
The glucocorticoid receptor regulates the binding of C/EPBbeta on the alpha-1-acid glycoprotein promoter in vivo.DNA Cell Biol. 1997 Dec;16(12):1467-76. doi: 10.1089/dna.1997.16.1467. DNA Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9428795
-
Dysfunctional glucocorticoid receptor with a single point mutation ablates the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-dependent growth suppression response in a steroid-resistant rat hepatoma cell variant.FASEB J. 1999 Jan;13(1):169-80. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.13.1.169. FASEB J. 1999. PMID: 9872941
-
How glucocorticoid receptors modulate the activity of other transcription factors: a scope beyond tethering.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Nov 5;380(1-2):41-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.12.014. Epub 2012 Dec 23. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23267834 Review.
-
[KAP-1, a scaffold protein in transcription regulation].Yi Chuan. 2007 Feb;29(2):131-6. doi: 10.1360/yc-007-0131. Yi Chuan. 2007. PMID: 17369165 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
TIF1beta/KAP-1 is a coactivator of the orphan nuclear receptor NGFI-B/Nur77.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 22;284(21):14147-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809023200. Epub 2009 Mar 25. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19321449 Free PMC article.
-
KAP1 targets actively transcribed genomic loci to exert pleomorphic effects on RNA polymerase II activity.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020 Mar 30;375(1795):20190334. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0334. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32068487 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM28 is required by the mouse KRAB domain protein ZFP568 to control convergent extension and morphogenesis of extra-embryonic tissues.Development. 2011 Dec;138(24):5333-43. doi: 10.1242/dev.072546. Development. 2011. PMID: 22110054 Free PMC article.
-
TEL/ETV6 binds to corepressor KAP1 via the HLH domain.Int J Hematol. 2006 Nov;84(4):377-80. doi: 10.1532/IJH97.06151. Int J Hematol. 2006. PMID: 17118767 No abstract available.
-
Transcriptome and Methylome Analysis Reveal Complex Cross-Talks between Thyroid Hormone and Glucocorticoid Signaling at Xenopus Metamorphosis.Cells. 2021 Sep 9;10(9):2375. doi: 10.3390/cells10092375. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aasland R, Gilson T J, Stewart A F. The PHD finger: implications for chromatin-mediated transcriptional regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995;20:56–59. - PubMed
-
- Barlow P N, Luisi B, Milner A, Elliott M, Everett R. Structure of the C3HC4 domain by 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. A new structural class of zinc-finger. J Mol Biol. 1994;237:201–211. - PubMed
-
- Baumann H, Firestone G L, Burgess T L, Gross K W, Yamamoto K R, Held W A. Dexamethasone regulation of α1-acid glycoprotein and other acute phase reactants in rat liver and hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983;258:563–570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
