Transcriptional regulation of the SMK1 mitogen-activated protein kinase gene during meiotic development in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 9742114
- PMCID: PMC109183
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.10.5970
Transcriptional regulation of the SMK1 mitogen-activated protein kinase gene during meiotic development in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
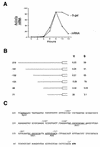
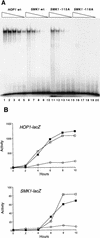
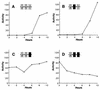
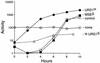
Meiotic development (sporulation) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is characterized by an ordered pattern of gene expression, with sporulation-specific genes classified as early, middle, mid-late, or late depending on when they are expressed. SMK1 encodes a mitogen-activated protein kinase required for spore morphogenesis that is expressed as a middle sporulation-specific gene. Here, we identify the cis-acting DNA elements that regulate SMK1 transcription and characterize the phenotypes of mutants with altered expression patterns. The SMK1 promoter contains an upstream activating sequence (UASS) that specifically interacts with the transcriptional activator Abf1p. The Abf1p-binding sites from the early HOP1 and the middle SMK1 promoters are functionally interchangeable, demonstrating that these elements do not play a direct role in their differential transcriptional timing. Timing of SMK1 expression is determined by another cis-acting DNA sequence termed MSE (for middle sporulation element). The MSE is required not only for activation of SMK1 transcription during middle sporulation but also for its repression during vegetative growth and early meiosis. In addition, the SMK1 MSE can repress vegetative expression in the context of the HOP1 promoter and convert HOP1 from an early to a middle gene. SMK1 function is not contingent on its tight transcriptional regulation as a middle sporulation-specific gene. However, promoter mutants with different quantitative defects in SMK1 transcript levels during middle sporulation show distinct sporulation phenotypes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RSC1 and RSC2 are required for expression of mid-late sporulation-specific genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Aug;3(4):910-8. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.4.910-918.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 15302824 Free PMC article.
-
The Ras/cAMP pathway and the CDK-like kinase Ime2 regulate the MAPK Smk1 and spore morphogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2009 Feb;181(2):511-23. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.098434. Epub 2008 Dec 15. Genetics. 2009. PMID: 19087957 Free PMC article.
-
The CDK-activating kinase CAK1 can dosage suppress sporulation defects of smk1 MAP kinase mutants and is required for spore wall morphogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.EMBO J. 1997 Mar 17;16(6):1305-17. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.6.1305. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9135146 Free PMC article.
-
Control of meiotic gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microbiol Rev. 1994 Mar;58(1):56-70. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.1.56-70.1994. Microbiol Rev. 1994. PMID: 8177171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meiosis: step-by-step through sporulation.Curr Biol. 1998 Jun 18;8(13):R461-3. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)70293-3. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9651674 Review.
Cited by
-
A phosphatase-centric mechanism drives stress signaling response.EMBO Rep. 2021 Nov 4;22(11):e52476. doi: 10.15252/embr.202152476. Epub 2021 Sep 24. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 34558777 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of critical interactions between Ndt80 and MSE DNA defining a novel family of Ig-fold transcription factors.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 May 25;32(9):2947-56. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh625. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15161958 Free PMC article.
-
The pachytene checkpoint in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires the Sum1 transcriptional repressor.EMBO J. 2000 Dec 1;19(23):6489-97. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.23.6489. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 11101521 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Recognition-like Motifs Activate a Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase.Biochemistry. 2018 Dec 18;57(50):6878-6887. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01032. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 30452242 Free PMC article.
-
The Ime2 protein kinase enhances the disassociation of the Sum1 repressor from middle meiotic promoters.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Aug;29(16):4352-62. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00305-09. Epub 2009 Jun 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19528232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alani E, Padmore R, Kleckner N. Analysis of wild-type and rad50 mutants of yeast suggest an intimate relationship between meiotic chromosome synapsis and recombination. Cell. 1990;61:419–436. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Smith J A, Seidmann J G, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons; 1987.
-
- Briza P, Breitenbach M, Ellinger A, Segall J. Isolation of two developmentally regulated genes involved in spore wall maturation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1990;4:1775–1789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
