Whole-cell and single-channel analysis of P-type calcium currents in cerebellar Purkinje cells of leaner mutant mice
- PMID: 9742139
- PMCID: PMC6793003
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-19-07687.1998
Whole-cell and single-channel analysis of P-type calcium currents in cerebellar Purkinje cells of leaner mutant mice
Abstract
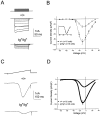
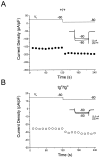
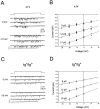
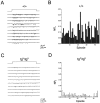
The leaner (tgla) mutation in mice results in severe ataxia and an overt neurodegeneration of the cerebellum. Positional cloning has revealed that the tgla mutation occurs in a gene encoding the voltage-activated calcium channel alpha1A subunit. The alpha1A subunit is highly expressed in the cerebellum and is thought to be the pore-forming subunit of P- and Q-type calcium channels. In this study we used both whole-cell and single-channel patch-clamp recordings to examine the functional consequences of the tgla mutation on P-type calcium currents. High-voltage-activated (HVA) calcium currents were recorded from acutely dissociated cerebellar Purkinje cells of homozygous leaner (tgla/tgla) and age-matched wild-type (+/+) mice. In whole cell recordings, we observed a marked reduction of peak current density in tgla/tgla Purkinje cells (-35.0 +/- 1.8 pA/pF) relative to that in +/+ (-103.1 +/- 5.9 pA/pF). The reduced whole-cell current in tgla/tgla cells was accompanied by little to no alteration in the voltage dependence of channel gating. In both genotypes, HVA currents were predominantly of the omega-agatoxin-IVA-sensitive P-type. Cell-attached patch-clamp recordings revealed no differences in single-channel conductance between the two genotypes and confirmed the presence of three distinct conductance levels (9, 13-14, and 17-18 pS) in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Analysis of patch open-probability (NPo) revealed a threefold reduction in the open-probability of channels in tgla/tgla patches (0.04 +/- 0.01) relative to that in +/+ (0.13 +/- 0.02), which may account for the reduced whole-cell current in tgla/tgla Purkinje cells. These results suggest that the tgla mutation can alter native P-type calcium channels at the single-channel level and that these alterations may contribute to the neuropathology of the leaner phenotype.
Figures




References
-
- Bean BP. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. - PubMed
-
- Berrow NS, Brice NL, Tedder I, Page KM, Dolphin AC. Properties of cloned rat α1A calcium channels transiently expressed in the COS-7 cell line. Eur J Neurosci. 1997;9:739–748. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaumer L, Campbell KP, Catterall WA, Harpold MM, Hofmann F, Horne WA, Mori Y, Schwartz A, Snutch TP, Tanabe T, Tsien RW. The naming of voltage-gated calcium channels. Neuron. 1994;13:505–506. - PubMed
-
- Catterall WA, Striessnig J. Receptor sites for Ca2+ channel antagonists. Trends Pharmacol. 1992;13:256–262. - PubMed
-
- Colquhoun D, Hawkes AG. Stochastic properties of ion channel openings and bursts in a membrane patch that contains two channels: evidence concerning the number of channels present when a record containing only single openings is observed. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 1990;240:453–477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
