Mast cells can secrete vascular permeability factor/ vascular endothelial cell growth factor and exhibit enhanced release after immunoglobulin E-dependent upregulation of fc epsilon receptor I expression
- PMID: 9743532
- PMCID: PMC2212544
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.188.6.1135
Mast cells can secrete vascular permeability factor/ vascular endothelial cell growth factor and exhibit enhanced release after immunoglobulin E-dependent upregulation of fc epsilon receptor I expression
Abstract
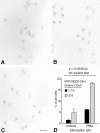
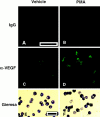
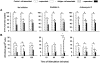
Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VPF/VEGF) can both potently enhance vascular permeability and induce proliferation of vascular endothelial cells. We report here that mouse or human mast cells can produce and secrete VPF/VEGF. Mouse mast cells release VPF/VEGF upon stimulation through Fcepsilon receptor I (FcepsilonRI) or c-kit, or after challenge with the protein kinase C activator, phorbol myristate acetate, or the calcium ionophore, A23187; such mast cells can rapidly release VPF/VEGF, apparently from a preformed pool, and can then sustain release by secreting newly synthesized protein. Notably, the Fc epsilonRI-dependent secretion of VPF/VEGF by either mouse or human mast cells can be significantly increased in cells which have undergone upregulation of Fc epsilonRI surface expression by a 4-d preincubation with immunoglobulin E. These findings establish that at least one cell type, the mast cell, can be stimulated to secrete VPF/VEGF upon immunologically specific activation via a member of the multichain immune recognition receptor family. Our observations also identify a new mechanism by which mast cells can contribute to enhanced vascular permeability and/or angiogenesis, in both allergic diseases and other settings.
Figures
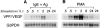

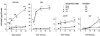
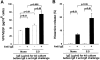
References
-
- Selye, H. 1965. The Mast Cells. Butterworth Inc., Washington, DC. 488 pp.
-
- Galli SJ, Zsebo KM, Geissler EN. The kit ligand, stem cell factor. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:1–96. - PubMed
-
- Glowacki J, Mulliken JB. Mast cells in hemangiomas and vascular malformations. Pediatrics. 1982;70:48–51. - PubMed
-
- Lauria de Cidre L, Sacerdote de Lustig E. Mast cell kinetics during tumor growth. Tumor Biol. 1990;11:196–201. - PubMed
-
- Starkey JR, Crowle PK, Taubenberger S. Mast-cell-deficient W/Wvmice exhibit a decreased rate of tumor angiogenesis. Int J Cancer. 1988;42:48–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

