Developmentally programmed assembly of higher order telomerase complexes with distinct biochemical and structural properties
- PMID: 9744868
- PMCID: PMC317169
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.18.2921
Developmentally programmed assembly of higher order telomerase complexes with distinct biochemical and structural properties
Abstract
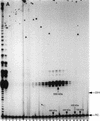
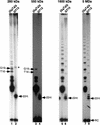
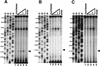
In Euplotes crassus, telomerase is responsible for telomere maintenance during vegetative growth and de novo telomere synthesis during macronuclear development. Here we show that telomerase in the vegetative stage of the life cycle exists as a 280-kD complex that can add telomeric repeats only onto telomeric DNA primers. Following the initiation of macronuclear development, telomerase assembles into larger complexes of 550 kD, 1600 kD, and 5 MD. In the 1600-kDa and 5-MDa complexes, telomerase is more processive than in the two smaller complexes and can add telomeres de novo onto nontelomeric 3' ends. Assembly of higher order telomerase complexes is accompanied by an extended region of RNase V1 and RNase T1 protection in the telomerase RNA subunit that is not observed with telomerase from vegetatively growing cells. The protected residues encompass a highly conserved region previously proposed to serve as a platform for formation of higher order structures. These findings provide the first direct demonstration of developmentally regulated higher order telomerase complexes with unique biochemical and structural properties.
Figures






References
-
- Beattie TL, Zhou W, Robinson MO, Harrington L. Reconstitution of human telomerase activity in vitro. Curr Biol. 1998;8:177–180. - PubMed
-
- Blasco MA, Funk W, Villeponteau B, Greider CW. Functional characterization and developmental regulation of mouse telomerase RNA. Science. 1995;269:1267–1270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
