Modulation of enzymatic activity and biological function of Listeria monocytogenes broad-range phospholipase C by amino acid substitutions and by replacement with the Bacillus cereus ortholog
- PMID: 9746585
- PMCID: PMC108596
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.10.4823-4831.1998
Modulation of enzymatic activity and biological function of Listeria monocytogenes broad-range phospholipase C by amino acid substitutions and by replacement with the Bacillus cereus ortholog
Abstract
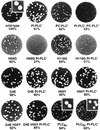
The secreted broad-range phosphatidylcholine (PC)-preferring phospholipase C (PC-PLC) of Listeria monocytogenes plays a role in the bacterium's ability to escape from phagosomes and spread from cell to cell. Based on comparisons with two orthologs, Clostridium perfringens alpha-toxin and Bacillus cereus PLC (PLCBc), we generated PC-PLC mutants with altered enzymatic activities and substrate specificities and analyzed them for biological function in tissue culture and mouse models of infection. Two of the conserved active-site zinc-coordinating histidines were confirmed by single amino acid substitutions H69G and H118G, which resulted in proteins inactive in broth culture and unstable intracellularly. Substitutions D4E and H56Y remodeled the PC-PLC active site to more closely resemble the PLCBc active site, while a gene replacement resulted in L. monocytogenes secreting PLCBc. All of these mutants yielded similar amounts of active enzyme as wild-type PC-PLC both in broth culture and intracellularly. D4E increased activity on and specificity for PC, while H56Y and D4E H56Y showed higher activity on both PC and sphingomyelin, with reduced specificity for PC. As expected, PLCBc expressed by L. monocytogenes was highly specific for PC. During early intracellular growth in human epithelial cells, the D4E mutant and the PLCBc-expressing strain performed significantly better than the wild type, while the H56Y and D4E H56Y mutants showed a significant defect. In assays for cell-to-cell spread, the H56Y and D4E mutants had close to wild-type characteristics, while the spreading efficiency of PLCBc was significantly lower. These studies emphasize the species-specific features of PC-PLC important for growth in mammalian cells.
Figures


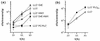

Similar articles
-
Expression and site-directed mutagenesis of the phosphatidylcholine-preferring phospholipase C of Bacillus cereus: probing the role of the active site Glu146.Biochemistry. 1996 Oct 1;35(39):12970-7. doi: 10.1021/bi961316f. Biochemistry. 1996. PMID: 8841144
-
Mutagenesis of active-site histidines of Listeria monocytogenes phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C: effects on enzyme activity and biological function.Infect Immun. 1999 Jan;67(1):182-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.1.182-186.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 9864213 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of the Listeria monocytogenes broad-range phospholipase PC-PLC during infection of human epithelial cells.J Bacteriol. 2003 Nov;185(21):6295-307. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.21.6295-6307.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 14563864 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylcholine-Specific Phospholipase C as a Promising Drug Target.Molecules. 2023 Jul 25;28(15):5637. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155637. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37570610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial phospholipases and intracellular growth: the two distinct phospholipases C of Listeria monocytogenes.Symp Ser Soc Appl Microbiol. 1998;27:7S-14S. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.1998.0840s107s.x. Symp Ser Soc Appl Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9750357 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Bacterial phospholipases C with dual activity: phosphatidylcholinesterase and sphingomyelinase.FEBS Open Bio. 2021 Dec;11(12):3262-3275. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13320. Epub 2021 Nov 8. FEBS Open Bio. 2021. PMID: 34709730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis for the unique molecular properties of broad-range phospholipase C from Listeria monocytogenes.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 14;14(1):6474. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42134-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37838694 Free PMC article.
-
The metalloprotease of Listeria monocytogenes controls cell wall translocation of the broad-range phospholipase C.J Bacteriol. 2005 Apr;187(8):2601-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.8.2601-2608.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15805506 Free PMC article.
-
pH-regulated activation and release of a bacteria-associated phospholipase C during intracellular infection by Listeria monocytogenes.Mol Microbiol. 2000 Jan;35(2):289-98. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01708.x. Mol Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10652090 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Listeria monocytogenes expressing anthrolysin O and phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Bacillus anthracis.Infect Immun. 2005 Oct;73(10):6639-46. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.10.6639-6646.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16177340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso, A. Personal communication.
-
- Bielecki J, Youngman P, Connelly P, Portnoy D A. Bacillus subtilis expressing a haemolysin gene from Listeria monocytogenes can grow in mammalian cells. Nature. 1990;345:175–176. - PubMed
-
- Bishop D K, Hinrichs D J. Adoptive transfer of immunity to Listeria monocytogenes: the influence of in vitro stimulation on lymphocyte subset requirements. J Immunol. 1987;139:2005–2009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

