Mannan-specific immunoglobulin G antibodies in normal human serum accelerate binding of C3 to Candida albicans via the alternative complement pathway
- PMID: 9746588
- PMCID: PMC108599
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.10.4845-4850.1998
Mannan-specific immunoglobulin G antibodies in normal human serum accelerate binding of C3 to Candida albicans via the alternative complement pathway
Abstract
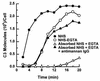
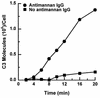
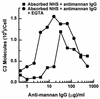
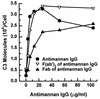
Candida albicans activates the classical and alternative complement pathways, leading to deposition of opsonic complement fragments on the cell surface. Our previous studies found that antimannan immunoglobulin G (IgG) in normal human serum (NHS) allows C. albicans to initiate the classical pathway. The purpose of this study was to determine whether antimannan IgG also plays a role in initiation of the alternative pathway. Pooled NHS was rendered free of classical pathway activity by chelation of serum Ca2+ with EGTA alone or in combination with immunoaffinity removal of antimannan antibodies. Kinetic analysis revealed a 6-min lag in detection of C3 binding to C. albicans incubated in EGTA-chelated NHS, compared to a 12-min lag in NHS that was both EGTA chelated and mannan absorbed. The 12-min lag was shortened to 6 min by addition of affinity-purified antimannan IgG. The accelerating effect of antimannan IgG on alternative pathway initiation was dose dependent and was reproduced in a complement binding reaction consisting of six purified proteins of the alternative pathway. Both Fab and F(ab')2 fragments of antimannan IgG facilitated alternative pathway initiation in a manner similar to that observed with intact antibody. Immunofluorescence analysis showed that addition of antimannan IgG to EGTA-chelated and mannan-absorbed serum promoted an early deposition of C3 molecules on the yeast cells but had little or no effect on distribution of the cellular sites for C3 activation. Thus, antimannan IgG antibodies play an important regulatory role in interactions between the host complement system and C. albicans.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characteristics of Fc-independent human antimannan antibody-mediated alternative pathway initiation of C3 deposition to Candida albicans.Mol Immunol. 2009 Jan;46(3):473-80. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.10.008. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Mol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19038459 Free PMC article.
-
Mannan-specific immunoglobulin G antibodies in normal human serum mediate classical pathway initiation of C3 binding to Candida albicans.Infect Immun. 1997 Sep;65(9):3822-7. doi: 10.1128/iai.65.9.3822-3827.1997. Infect Immun. 1997. PMID: 9284158 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of IgG Subclass on Human Antimannan Antibody-Mediated Resistance to Hematogenously Disseminated Candidiasis in Mice.Infect Immun. 2015 Nov 16;84(2):386-94. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00890-15. Print 2016 Feb. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26573736 Free PMC article.
-
Defining criteria for anti-mannan antibodies to protect against candidiasis.Curr Mol Med. 2005 Jun;5(4):383-92. doi: 10.2174/1566524054022576. Curr Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 15977994 Review.
-
Combined use of nonculture-based lab techniques in the diagnosis and management of critically ill patients with invasive fungal infections.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012 Nov;10(11):1321-30. doi: 10.1586/eri.12.128. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012. PMID: 23241189 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of human plasma proteins associated with the cell wall of the pathogenic fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2013 Apr;341(2):87-95. doi: 10.1111/1574-6968.12097. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23398536 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of Fc-independent human antimannan antibody-mediated alternative pathway initiation of C3 deposition to Candida albicans.Mol Immunol. 2009 Jan;46(3):473-80. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.10.008. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Mol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19038459 Free PMC article.
-
The pH-regulated antigen 1 of Candida albicans binds the human complement inhibitor C4b-binding protein and mediates fungal complement evasion.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 11;286(10):8021-8029. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.130138. Epub 2011 Jan 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21212281 Free PMC article.
-
Contrasting roles of mannan-specific monoclonal immunoglobulin M antibodies in the activation of classical and alternative pathways by Candida albicans.Infect Immun. 1998 Dec;66(12):6027-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.12.6027-6029.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9826391 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Candida albicans and the mammalian innate host defense.Infect Immun. 2012 Apr;80(4):1304-13. doi: 10.1128/IAI.06146-11. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22252867 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albar J P, Juarez C, Vivanco-Martinez F, Bragado R, Ortiz F. Structural requirements of rabbit IgG F(ab′)2 fragment for activation of the complement system through the alternative pathway. I. disulfide bonds. Mol Immunol. 1981;18:925–934. - PubMed
-
- Bjornson A B, Lobel J S. Lack of a requirement for the Fc region of IgG in restoring pneumococcal opsonization via the alternative complement pathway in sickle cell disease. J Infect Dis. 1986;154:760–769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

