Antigenic analysis of Bordetella pertussis filamentous hemagglutinin with phage display libraries and rabbit anti-filamentous hemagglutinin polyclonal antibodies
- PMID: 9746593
- PMCID: PMC108604
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.10.4884-4894.1998
Antigenic analysis of Bordetella pertussis filamentous hemagglutinin with phage display libraries and rabbit anti-filamentous hemagglutinin polyclonal antibodies
Abstract
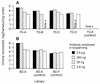
Although substantial advancements have been made in the development of efficacious acellular vaccines against Bordetella pertussis, continued progress requires better understanding of the antigenic makeup of B. pertussis virulence factors, including filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA). To identify antigenic regions of FHA, phage display libraries constructed by using random fragments of the 10-kbp EcoRI fragment of B. pertussis fhaB were affinity selected with rabbit anti-FHA polyclonal antibodies. Characterization of antibody-reactive clones displaying FHA-derived peptides identified 14 antigenic regions, each containing one or more epitopes. A number of clones mapped within regions containing known or putative FHA adhesin domains and may be relevant for the generation of protective antibodies. The immunogenic potential of the phage-displayed peptides was assessed indirectly by comparing their recognition by antibodies elicited by sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-denatured and native FHA and by measuring the inhibition of this recognition by purified FHA. FHA residues 1929 to 2019 may contain the most dominant linear epitope of FHA. Clones mapping to this region accounted for ca. 20% of clones recovered from the initial library selection and screening procedures. They are strongly recognized by sera against both SDS-denatured and native FHA, and this recognition is readily inhibited by purified FHA. Given also that this region includes a factor X homolog (J. Sandros and E. Tuomanen, Trends Microbiol. 1:192-196, 1993) and that the single FHA epitope (residues 2001 to 2015) was unequivocally defined in a comparable study by E. Leininger et al. (J. Infect. Dis. 175:1423-1431, 1997), peptides derived from residues of 1929 to 2019 of FHA are strong candidates for future protection studies.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cloning and immunologic characterization of a truncated Bordetella bronchiseptica filamentous hemagglutinin fusion protein.Vaccine. 1999 Dec 10;18(9-10):860-7. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(99)00322-9. Vaccine. 1999. PMID: 10580199
-
Eighty-kilodalton N-terminal moiety of Bordetella pertussis filamentous hemagglutinin: adherence, immunogenicity, and protective role.Infect Immun. 2002 Aug;70(8):4142-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4142-4147.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12117922 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and characterization of single-chain variable fragment antibodies directed against the Bordetella pertussis surface adhesins filamentous hemagglutinin and pertactin.Infect Immun. 2007 Nov;75(11):5476-82. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00494-07. Epub 2007 Aug 27. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17724067 Free PMC article.
-
Bordetella filamentous hemagglutinin and fimbriae: critical adhesins with unrealized vaccine potential.Pathog Dis. 2015 Nov;73(8):ftv079. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv079. Epub 2015 Sep 27. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26416077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Substantial gaps in knowledge of Bordetella pertussis antibody and T cell epitopes relevant for natural immunity and vaccine efficacy.Hum Immunol. 2014 May;75(5):440-51. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2014.02.013. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Hum Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24530743 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fusion expression and immunogenicity of Bordetella pertussis PTS1-FHA protein: implications for the vaccine development.Mol Biol Rep. 2011 Mar;38(3):1957-63. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0317-6. Epub 2010 Sep 28. Mol Biol Rep. 2011. PMID: 20878241
-
Natural-host animal models indicate functional interchangeability between the filamentous haemagglutinins of Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica and reveal a role for the mature C-terminal domain, but not the RGD motif, during infection.Mol Microbiol. 2009 Mar;71(6):1574-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06623.x. Epub 2009 Feb 10. Mol Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19220744 Free PMC article.
-
Expression, Purification and Characterization of Three Overlapping Immunodominant Recombinant Fragments from Bordetella pertussis Filamentous Hemagglutinin.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2013 Jan;5(1):20-8. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23626873 Free PMC article.
-
Haemagglutination induced by Bordetella pertussis filamentous haemagglutinin adhesin (FHA) is inhibited by antibodies produced against FHA(430-873) fragment expressed in Lactobacillus casei.Curr Microbiol. 2006 Dec;53(6):462-6. doi: 10.1007/s00284-005-0388-0. Epub 2006 Nov 13. Curr Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17106803
-
Virus-like particles displaying the mature C-terminal domain of filamentous hemagglutinin are immunogenic and protective against Bordetella pertussis respiratory infection in mice.Infect Immun. 2024 Aug 13;92(8):e0027024. doi: 10.1128/iai.00270-24. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Infect Immun. 2024. PMID: 39023271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brennan M J, Burns D L, Meade B D, Shahin R D, Manclark C R. Recent advances in the development of pertussis vaccines. In: Ellis R, editor. Vaccines: new approaches to immunological problems. Shoreham, Mass: Butterworth; 1992. pp. 23–52. - PubMed
-
- Brennan M J, Shahin R D. Pertussis antigens that abrograte bacterial adherence and elicit immunity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;154:S145–S149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

