Cloning and molecular characterization of a cDNA clone coding for Trichomonas vaginalis alpha-actinin and intracellular localization of the protein
- PMID: 9746598
- PMCID: PMC108609
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.10.4924-4931.1998
Cloning and molecular characterization of a cDNA clone coding for Trichomonas vaginalis alpha-actinin and intracellular localization of the protein
Abstract
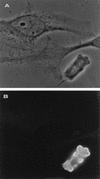
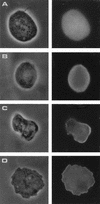
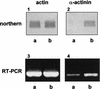
We have identified and sequenced a cDNA clone coding for Trichomonas vaginalis alpha-actinin. Analysis of the obtained sequence revealed that the 2,857-nucleotide-long cDNA contained an open reading frame encoding 849 amino acids which showed consistent homology with alpha-actinins of different species. Such homology was particularly significant in regions which have been reported to represent the actin-binding and Ca2+-binding domains in other alpha-actinins. The deduced protein was also characterized by the presence of a divergent central region thought to play a role in its high immunogenicity. A study of protein localization performed by immunofluorescence revealed that the protein is diffusely distributed throughout the T. vaginalis cytoplasm when the cell is pear shaped. When parasites adhere and transform into the amoeboid morphology, the protein is located only in areas close to the cytoplasmic membrane and colocalizes with actin. Concomitantly with transformation into the amoeboid morphology, alpha-actinin mRNA expression is upregulated.
Figures


References
-
- Addis M F, Rappelli P, Cappuccinelli P, Fiori P L. Extracellular release by Trichomonas vaginalis of a NADP+ dependent malic enzyme involved in pathogenicity. Microb Pathog. 1997;23:55–61. - PubMed
-
- Addis, M. F., et al. Unpublished data.
-
- Arroyo R, Engbring J, Alderete J F. Molecular basis of host epithelial cell recognition by Trichomonas vaginalis. Mol Microbiol. 1992;6:853–862. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

