Mutational analysis of superantigen activity responsible for the induction of skin erythema by streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin C
- PMID: 9746612
- PMCID: PMC108623
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.10.5020-5026.1998
Mutational analysis of superantigen activity responsible for the induction of skin erythema by streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin C
Abstract
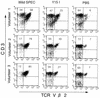
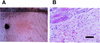
Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin C (SPEC), when injected intradermally, induces erythema in unsensitized rabbits. In the present study, we examined whether this erythema induction is due to the T-cell stimulatory activity of SPEC as a superantigen. Analysis by using single-residue mutant SPECs indicated that mutant SPECs Y15I, A16E, and Y17I, in which tyrosine 15, alanine 16, and tyrosine 17 were replaced with isoleucine, glutamic acid, and isoleucine, respectively, exhibited significantly reduced mitogenic activity for Vbeta2(+) human T cells in vitro, and Y15I showed as much as a 1, 000-fold reduction. Y15I mutant SPEC, however, retained the ability to bind to major histocompatibility complex class II antigen and to form a homodimer, implying that residue 15 is critically important for the interaction of SPEC with T-cell antigen receptor beta chains. When injected intradermally into normal rabbits, wild-type SPEC induced a characteristic erythema after 3 h in a dose-dependent fashion, which was associated with polymorphonuclear and mononuclear cell infiltration. This erythema formation was found to be severely suppressed by systemic pretreatment with cyclosporin A, suggesting the involvement of host T cells. Y15I mutant SPEC exhibited nearly 1, 000-fold less erythema induction in vivo than wild-type SPEC. Altogether, the present results strongly suggest that erythema induction in rabbits by SPEC is attributable mostly to its T-cell stimulatory activity as a superantigen.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Pyrogenicity and cytokine-inducing properties of Streptococcus pyogenes superantigens: comparative study of streptococcal mitogenic exotoxin Z and pyrogenic exotoxin A.Infect Immun. 2001 Jun;69(6):4141-5. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.6.4141-4145.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11349089 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin J, a novel superantigen.Infect Immun. 2001 Mar;69(3):1381-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.3.1381-1388.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11179302 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the recognition of superantigen streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A (SpeA1) by MHC class II molecules and T-cell receptors.EMBO J. 1999 Jan 4;18(1):9-21. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.1.9. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 9878045 Free PMC article.
-
Superantigens and pseudosuperantigens of gram-positive cocci.Med Microbiol Immunol. 1995 May;184(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/BF00216783. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1995. PMID: 8538573 Review.
-
Streptococcal superantigen, mitogenic factor, and pyrogenic exotoxin B expressed by Streptococcus pyogenes. Structure and function.Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 1997 May-Aug;27(2-3):143-72. doi: 10.1080/10826069708000074. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 1997. PMID: 9292924 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Incidence and Characteristics of Scarlet Fever, South Korea, 2008-2015.Emerg Infect Dis. 2017 Apr;23(4):658-661. doi: 10.3201/eid2304.160773. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28322696 Free PMC article.
-
SpeS: A Novel Superantigen and Its Potential as a Vaccine Adjuvant against Strangles.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 23;21(12):4467. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124467. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32586031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya K R, Passalacqua E F, Jones E Y, Harlos K, Stuart D I, Brehm R D, Tranter H S. Structural basis of superantigen action inferred from crystal structure of toxic-shock syndrome toxin-1. Nature. 1994;367:94–97. - PubMed
-
- Alber G, Hammer D K, Fleischer B. Relationship between enterotoxic- and lymphocyte-stimulating activity of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J Immunol. 1990;144:4501–4504. - PubMed
-
- Betley M J, Borst D W, Legassa L B. Staphylococcal enterotoxins, toxic shock syndrome toxin and streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins: a comparative study of their molecular biology. Chem Immunol. 1992;55:1–35. - PubMed
-
- Betley M J, Miller V L, Mekalanos J J. Genetics of bacterial enterotoxins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:577–605. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

