Characterization of an A-factor-responsive repressor for amfR essential for onset of aerial mycelium formation in Streptomyces griseus
- PMID: 9748440
- PMCID: PMC107543
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.19.5085-5093.1998
Characterization of an A-factor-responsive repressor for amfR essential for onset of aerial mycelium formation in Streptomyces griseus
Abstract
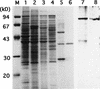
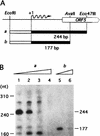
A-factor (2-isocapryloyl-3R-hydroxymethyl-gamma-butyrolactone) is essential for the initiation of aerial mycelium formation in Streptomyces griseus. amfR is one of the genes which, when cloned on a low-copy-number plasmid, suppresses the aerial mycelium-negative phenotype of an A-factor-deficient mutant of S. griseus. Disruption of the chromosomal amfR gene resulted in complete abolition of aerial mycelium formation, indicating that amfR is essential for the onset of morphogenesis. Cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the region upstream of amfR predicted an operon consisting of orf5, orf4, and amfR. Consistent with this idea, Northern blotting and S1 mapping analyses suggested that these three genes were cotranscribed mainly by a promoter (PORF5) in front of orf5. Furthermore, PORF5 was active only in the presence of A-factor, indicating that it is A-factor dependent. Gel mobility shift assays showed the presence of a protein (AdpB) able to bind PORF5 in the cell extract from an A-factor-deficient mutant but not from the wild-type strain. AdpB was purified to homogeneity and found to bind specifically to the region from -72 to -44 bp with respect to the transcriptional start point. Runoff transcriptional analysis of PORF5 with purified AdpB and an RNA polymerase complex isolated from vegetative mycelium showed that AdpB repressed the transcription in a concentration-dependent manner. It is thus apparent that AmfR as a switch for aerial mycelium formation and AdpB as a repressor for amfR are members in the A-factor regulatory cascade, leading to morphogenesis.
Figures





References
-
- Babcock M J, Kendrick K E. Transcriptional and translational features of a sporulation gene of Streptomyces griseus. Gene. 1990;95:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Beck E, Ludwig G, Auerswald E A, Reiss B, Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and exact localisation of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene. 1982;19:327–336. - PubMed
-
- Bibb M J, Findlay P R, Johnson M W. The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene. 1984;30:157–166. - PubMed
-
- Chater K F. Morphological and physiological differentiation in Streptomyces. In: Losick R, Shapiro L, editors. Microbial development. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1984. pp. 89–115.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

