Roles of the Escherichia coli small heat shock proteins IbpA and IbpB in thermal stress management: comparison with ClpA, ClpB, and HtpG In vivo
- PMID: 9748451
- PMCID: PMC107554
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.19.5165-5172.1998
Roles of the Escherichia coli small heat shock proteins IbpA and IbpB in thermal stress management: comparison with ClpA, ClpB, and HtpG In vivo
Abstract
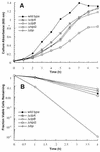
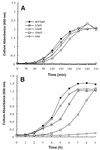
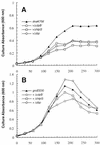
We have constructed an Escherichia coli strain lacking the small heat shock proteins IbpA and IbpB and compared its growth and viability at high temperatures to those of isogenic cells containing null mutations in the clpA, clpB, or htpG gene. All mutants exhibited growth defects at 46 degrees C, but not at lower temperatures. However, the clpA, htpG, and ibp null mutations did not reduce cell viability at 50 degrees C. When cultures were allowed to recover from transient exposure to 50 degrees C, all mutations except Deltaibp led to suboptimal growth as the recovery temperature was raised. Deletion of the heat shock genes clpB and htpG resulted in growth defects at 42 degrees C when combined with the dnaK756 or groES30 alleles, while the Deltaibp mutation had a detrimental effect only on the growth of dnaK756 mutants. Neither the overexpression of these heat shock proteins nor that of ClpA could restore the growth of dnaK756 or groES30 cells at high temperatures. Whereas increased levels of host protein aggregation were observed in dnaK756 and groES30 mutants at 46 degreesC compared to wild-type cells, none of the null mutations had a similar effect. These results show that the highly conserved E. coli small heat shock proteins are dispensable and that their deletion results in only modest effects on growth and viability at high temperatures. Our data also suggest that ClpB, HtpG, and IbpA and -B cooperate with the major E. coli chaperone systems in vivo.
Figures
References
-
- Alexeyev M F. Three kanamycin resistance gene cassettes with different polylinkers. BioTechniques. 1995;18:52–56. - PubMed
-
- Baneyx F, Gatenby A A. A mutation in GroEL interferes with protein folding by reducing the rate of discharge of sequestered polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:11637–11644. - PubMed
-
- Chuang S-E, Burland V, Plunkett III G, Daniels D L, Blattner F R. Sequence analysis of four new heat-shock genes constituting the hslTS/ibpAB and hslVU operons in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1993;134:1–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

