Proteolytic activation of PKN by caspase-3 or related protease during apoptosis
- PMID: 9751706
- PMCID: PMC21681
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.20.11566
Proteolytic activation of PKN by caspase-3 or related protease during apoptosis
Abstract
PKN, a fatty acid- and Rho-activated serine/threonine kinase having a catalytic domain highly homologous to protein kinase C (PKC), was cleaved at specific sites in apoptotic Jurkat and U937 cells on Fas ligation and treatment with staurosporin or etoposide, respectively. The cleavage of PKN occurred with a time course similar to that of PKCdelta, a known caspase substrate. This proteolysis was inhibited by a caspase inhibitor, acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-aldehyde. The cleavage fragments were generated in vitro from PKN by treatment with recombinant caspase-3. Site-directed mutagenesis of specific aspartate residues prevented the appearance of these fragments. These results indicate that PKN is cleaved by caspase-3 or related protease during apoptosis. The major proteolysis took place between the amino-terminal regulatory domain and the carboxyl-terminal catalytic domain, and it generated a constitutively active kinase fragment. The cleavage of PKN may contribute to signal transduction, eventually leading to apoptosis.
Figures
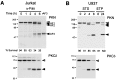
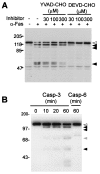

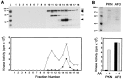

References
-
- Mukai H, Ono Y. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;199:897–904. - PubMed
-
- Mukai H, Kitagawa M, Shibata H, Takanaga H, Mori K, Shimakawa M, Miyahara M, Hirao K, Ono Y. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;204:348–356. - PubMed
-
- Mukai H, Mori K, Takanaga H, Kitagawa M, Shibata H, Shimakawa M, Miyahara M, Ono Y. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1261:296–300. - PubMed
-
- Palmer R H, Ridden J, Parker P J. Eur J Biochem. 1995;227:344–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

