A method for DNA extraction from the desert cyanobacterium chroococcidiopsis and its application to identification of ftsZ
- PMID: 9758840
- PMCID: PMC106599
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.64.10.4053-4056.1998
A method for DNA extraction from the desert cyanobacterium chroococcidiopsis and its application to identification of ftsZ
Abstract
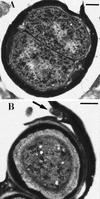
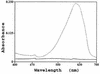
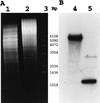
A method was developed for extraction of DNA from Chroococcidiopsis that overcomes obstacles posed by bacterial contamination and the presence of a thick envelope surrounding the cyanobacterial cells. The method is based on the resistance of Chroococcidiopsis to lysozyme and consists of a lysozyme treatment followed by osmotic shock that reduces the bacterial contamination by 3 orders of magnitude. Then DNase treatment is performed to eliminate DNA from the bacterial lysate. Lysis of Chroococcidiopsis cells is achieved by grinding with glass beads in the presence of hot phenol. Extracted DNA is further purified by cesium-chloride density gradient ultracentrifugation. This method permitted the first molecular approach to the study of Chroococcidiopsis, and a 570-bp fragment of the gene ftsZ was cloned and sequenced.
Figures
References
-
- Angeloni S V, Potts M. Purification of polysomes from a lysozyme-resistant desiccation-tolerant cyanobacterium. J Microbiol Methods. 1987;6:61–69.
-
- Billi D. Ph.D. thesis. Rome, Italy: University of Rome Tor Vergata; 1996.
-
- Billi D, Grilli Caiola M. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus deprivation on Chroococcidiopsis sp. (Chroococcales) Algol Stud. 1996;83:93–105.
-
- Billi D, Grilli Caiola M. Effects of nitrogen limitation and starvation on Chroococcidiopsis sp. (Chroococcales) New Phytol. 1996;133:563–571.
-
- Buikema W J, Haselkorn R. Molecular genetics of cyanobacterial development. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1993;44:33–52.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

