Use of phospholipid fatty acids and carbon source utilization patterns To track microbial community succession in developing compost
- PMID: 9758843
- PMCID: PMC106602
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.64.10.4062-4064.1998
Use of phospholipid fatty acids and carbon source utilization patterns To track microbial community succession in developing compost
Abstract
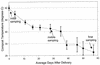
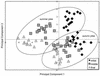
Carbon source utilization and phospholipid fatty acid analyses were used to track the rapidly changing microbial community in composting dairy waste. Microbial abilities to utilize common plant sugars increased during composting. Community phospholipid profiles changed significantly over time. Phospholipids suggested the presence of more thermophiles and fewer bacteria with continued compost development.
Figures
References
-
- Chang Y, Hudson H J. The fungi of wheat straw compost. Trans Br Mycol Soc. 1967;50:649–666.
-
- Federle T W. Microbial distribution in soil—new techniques. In: Megusar F, Gantar M, editors. Perspectives in microbial ecology. Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Microbial Ecology. Ljubljana, Slovenia: Slovene Society for Microbiology; 1986. pp. 493–498.
-
- Fulco A J, Fujii D K. Adaptive regulation of membrane lipid biosynthesis in Bacilli by environmental temperature. In: Kates M, Kuksis A, editors. Membrane fluidity: biophysical techniques and cellular regulation. Totowa, N.J: Humana Press; 1980. pp. 77–98.
-
- Garland J L, Mills A L. A community-level physiological approach for studying microbial communities. In: Ritz K, et al., editors. Beyond the biomass: compositional and functional analysis of soil microbial communities. New York, N.Y: John Wiley; 1994. pp. 77–83.
-
- Guckert J B, Antworth C P, Nichols P D, White D C. Phospholipid, ester-linked fatty acid profiles as reproducible assays for changes in prokaryotic community structure of estuarine sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 1985;31:147–158.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical