Receptor editing occurs frequently during normal B cell development
- PMID: 9763602
- PMCID: PMC2212498
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.188.7.1231
Receptor editing occurs frequently during normal B cell development
Abstract
Allelic exclusion is established in development through a feedback mechanism in which the assembled immunoglobulin (Ig) suppresses further V(D)J rearrangement. But Ig expression sometimes fails to prevent further rearrangement. In autoantibody transgenic mice, reactivity of immature B cells with autoantigen can induce receptor editing, in which allelic exclusion is transiently prevented or reversed through nested light chain gene rearrangement, often resulting in altered B cell receptor specificity. To determine the extent of receptor editing in a normal, non-Ig transgenic immune system, we took advantage of the fact that lambda light chain genes usually rearrange after kappa genes. This allowed us to analyze kappa loci in IgMlambda+ cells to determine how frequently in-frame kappa genes fail to suppress lambda gene rearrangements. To do this, we analyzed recombined VkappaJkappa genes inactivated by subsequent recombining sequence (RS) rearrangement. RS rearrangements delete portions of the kappa locus by a V(D)J recombinase-dependent mechanism, suggesting that they play a role in receptor editing. We show that RS recombination is frequently induced by, and inactivates, functionally rearranged kappa loci, as nearly half (47%) of the RS-inactivated VkappaJkappa joins were in-frame. These findings suggest that receptor editing occurs at a surprisingly high frequency in normal B cells.
Figures


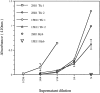
References
-
- Coleclough C, Perry RP, Karjalainen K, Weigert M. Aberrant rearrangements contribute significantly to the allelic exclusion of immunoglobulin gene expression. Nature. 1981;290:372–378. - PubMed
-
- Nussenzweig MC, Shaw AC, Sinn E, Danner DB, Holmes KL, Morse HC, III, Leder P. Allelic exclusion in transgenic mice that express the membrane form of immunoglobulin μ. Science. 1987;236:816–819. - PubMed
-
- Ritchie KA, Brinster RL, Storb U. Allelic exclusion and control of endogenous immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in κ transgenic mice. Nature. 1984;312:517–520. - PubMed
-
- Storb, U. 1995. Ig gene expression and regulation in Ig transgenic mice. In Immunoglobulin Genes. Second Edition. T. Honjo and F.W. Alt, editors. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. 345–363.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

