Costimulatory molecules in Wegener's granulomatosis (WG): lack of expression of CD28 and preferential up-regulation of its ligands B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86) on T cells
- PMID: 9764612
- PMCID: PMC1905085
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00695.x
Costimulatory molecules in Wegener's granulomatosis (WG): lack of expression of CD28 and preferential up-regulation of its ligands B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86) on T cells
Abstract
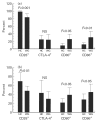
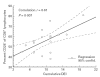
T cells are most likely to play an important role in the pathogenesis of WG, and recently a predominant Th1 pattern of immune response has been demonstrated in granulomatous inflammation. Since the expression of costimulatory molecules has a significant impact on the cytokine profile and proliferation response of T cells, the goal of this study was to characterize the expression of costimulatory molecules (CD28, CTLA-4 (CD152), B7-1 (CD80), B7-2 (CD86)) on T cells, monocytes and B cells in WG, and to correlate the findings with clinical parameters such as disease activity, extent and therapy. WG patients (n = 24) and healthy controls (HC; n = 17) were examined for the expression of costimulatory molecules by fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis, both in whole peripheral blood and after in vitro activation of T cells and antigen-presenting cells. Results were correlated with clinical data. The expression of CD28 on CD4+ and CD8+ cells was significantly lower in WG than in HC (CD28+ 81.4% in WG versus 97.9% of CD4+ cells (P < 0.0001); CD28+ 44.6% in WG versus 68.5% of CD8+ cells (P < 0.00001)), both in peripheral blood and after in vitro activation. A lower percentage of monocytes was B7-2+ in WG than in HC in peripheral blood, whereas no significant differences in the expression of B7-1 and B7-2 were observed after in vitro stimulation of monocytes and B cells. After in vitro activation a significantly higher percentage of B7-1+ and B7-2+ T cells was seen in WG. There was no significant difference in the CTLA-4 expression pattern between WG and HC. The percentage of CD28+ lymphocytes correlated negatively with the Disease Extent Index cumulated over the course of disease (r = -0.46, P = 0.03), indicating a more severe manifestation in patients with lower CD28 expression. Correlations with other clinical parameters such as activity or therapy were not seen. WG patients show a lack of CD28 expression on T cells and an unusual up-regulation of its ligands B7-1 and B7-2 on T cells after in vitro activation as well as a lower expression of B7-2 on freshly isolated monocytes compared with HC. These features might promote the Th1 cytokine pattern and thereby contribute to persistently high levels of immune activation in WG.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of costimulatory molecules CD80 and CD86 and their receptors CD28, CTLA-4 on malignant ascites CD3+ tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) from patients with ovarian and other types of peritoneal carcinomatosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2000 Jan;119(1):19-27. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01105.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10606960 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of CTLA-4 (CD152) by T and B lymphocytes in Wegener's granulomatosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2001 Oct;126(1):143-50. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01575.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11678911 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of costimulatory molecules on peripheral blood monocytes in patients with Crohn's disease.Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997 Dec;32(12):1241-6. doi: 10.3109/00365529709028154. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997. PMID: 9438323
-
CD80, CD86 and CD40 provide accessory signals in a multiple-step T-cell activation model.Immunol Rev. 1996 Oct;153:47-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1996.tb00920.x. Immunol Rev. 1996. PMID: 9010719 Review.
-
Regulation of T and B cell responses by modulating interactions between CD28/CTLA4 and their ligands, CD80 and CD86.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997 Apr 5;815:392-400. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1997.tb52090.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997. PMID: 9186685 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis of ANCA-Associated Pulmonary Vasculitis.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Aug;39(4):413-424. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1673386. Epub 2018 Nov 7. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 30404109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripheral blood and granuloma CD4(+)CD28(-) T cells are a major source of interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in Wegener's granulomatosis.Am J Pathol. 2002 May;160(5):1717-24. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)61118-2. Am J Pathol. 2002. PMID: 12000723 Free PMC article.
-
T-helper cells as new players in ANCA-associated vasculitides.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011 Aug 23;13(4):236. doi: 10.1186/ar3362. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 21888687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct tumour necrosis factor alpha, interferon gamma, interleukin 10, and cytotoxic T cell antigen 4 gene polymorphisms in disease occurrence and end stage renal disease in Wegener's granulomatosis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Mar;64(3):457-61. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.025809. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. PMID: 15708894 Free PMC article.
-
What you should know about PR3-ANCA. Evidence for the role of T cells in the pathogenesis of systemic vasculitis.Arthritis Res. 2000;2(4):260-2. doi: 10.1186/ar98. Epub 2000 Jun 12. Arthritis Res. 2000. PMID: 11094438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Csernok E, Müller A, Wang G, Trabandt A, Paulsen J, Schnabel A, Gross WL. Cytokine profiles in Wegener's granulomatosis: predominance of type-1 (Th1) in the granulomatous inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 in press. - PubMed
-
- Schlesier M, Kaspar T, Gutfleisch J, Wolff-Vorbeck G, Peter HH. Activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cell subsets in Wegener's granulomatosis. Rheumatol Int. 1995;14:213–9. - PubMed
-
- Schmitt WH, Heesen C, Csernok E, Rautmann A, Gross WL. Elevated serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor in patients with Wegener's granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992;35:1088–96. - PubMed
-
- Wang G, Hansen H, Tatsis E, Csernok E, Gross WL. High plasma levels of soluble form of CD30 activation molecule reflect disease activity in patients with Wegener's granulomatosis. Am J Med. 1997;102:517–23. - PubMed
-
- Martens PB, Goronzy JJ, Schaid D, Weyand WM. Expansion of unusual CD4+ T cells in severe rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:1106–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

