Dissemination of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus from the gastric mucosa requires G protein-coupled signaling
- PMID: 9765400
- PMCID: PMC110272
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.11.8613-8619.1998
Dissemination of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus from the gastric mucosa requires G protein-coupled signaling
Abstract
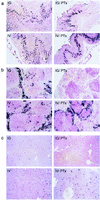
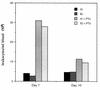
The gastric mucosa is an important portal of entry for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infections. Within hours after intragastric (i.g.) inoculation, virus appears in the gastric epithelia, then in the mesenteric lymph nodes and spleen, and then in the liver and brain. By 72 h i.g.-inoculated virus is widely disseminated and equivalent to intravenous (i.v.) infection (S. K. Rai, B. K. Micales, M. S. Wu, D. S. Cheung, T. D. Pugh, G. E. Lyons, and M. S. Salvato. Am. J. Pathol. 151:633-639, 1997). Pretreatment of mice with a G protein inhibitor, pertussis toxin (PTx), delays LCMV dissemination after i.g., but not after i.v., inoculation. Delayed infection was confirmed by plaque assays, by reverse transcription-PCR, and by in situ hybridization. The differential PTx effect on i.v. and i.g. infections indicates that dissemination from the gastric mucosa requires signals transduced through heterotrimeric G protein complexes. PTx has no direct effect on LCMV replication, but it modulates integrin expression in part by blocking chemokine signals. LCMV infection of macrophages up-regulates CD11a, and PTx treatment counteracts this. PTx may prevent early LCMV dissemination by inhibiting the G protein-coupled chemotactic response of macrophages infected during the initial exposure, thus blocking systemic virus spread.
Figures


References
-
- Andersson E C, Christensen J P, Marker O, Thomsen A R. Changes in cell adhesion molecule expression on T cells associated with systemic virus infection. J Immunol. 1994;152:1237–1245. - PubMed
-
- Andersson E C, Christensen J P, Scheynius A, Marker O, Thomsen A R. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection is associated with long-standing perturbation of LFA-1 expression on CD8+ T cells. Scand J Immunol. 1995;42:110–118. - PubMed
-
- Brankin B, Hart M N, Cosby S L, Fabry Z, Allen I V. Adhesion molecule expression and lymphocyte adhesion to cerebral endothelium: effects of measles virus and herpes simplex 1 virus. J Neuroimmunol. 1995;56:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Campbell J J, Hedrick J, Zlotnik A, Siani M A, Thompson D A, Butcher E C. Chemokines and the arrest of lymphocytes rolling under flow conditions. Science. 1998;279:381–384. - PubMed
-
- Chirgwin J M, Przybyla A E, MacDonald R J, Rutter W J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979;18:5294–5299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

