Tat protein induces human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) coreceptors and promotes infection with both macrophage-tropic and T-lymphotropic HIV-1 strains
- PMID: 9765440
- PMCID: PMC110312
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.11.8952-8960.1998
Tat protein induces human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) coreceptors and promotes infection with both macrophage-tropic and T-lymphotropic HIV-1 strains
Abstract
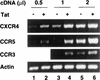
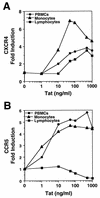
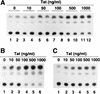
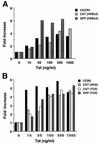
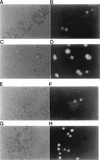
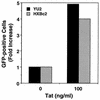
Chemokine receptors CCR5 and CXCR4 are the primary fusion coreceptors utilized for CD4-mediated entry by macrophage (M)- and T-cell line (T)-tropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) strains, respectively. Here we demonstrate that HIV-1 Tat protein, a potent viral transactivator shown to be released as a soluble protein by infected cells, differentially induced CXCR4 and CCR5 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. CCR3, a less frequently used coreceptor for certain M-tropic strains, was also induced. CXCR4 was induced on both lymphocytes and monocytes/macrophages, whereas CCR5 and CCR3 were induced on monocytes/macrophages but not on lymphocytes. The pattern of chemokine receptor induction by Tat was distinct from that by phytohemagglutinin. Moreover, Tat-induced CXCR4 and CCR5 expression was dose dependent. Monocytes/macrophages were more susceptible to Tat-mediated induction of CXCR4 and CCR5 than lymphocytes, and CCR5 was more readily induced than CXCR4. The concentrations of Tat effective in inducing CXCR4 and CCR5 expression were within the picomolar range and close to the range of extracellular Tat observed in sera from HIV-1-infected individuals. The induction of CCR5 and CXCR4 expression correlated with Tat-enhanced infectivity of M- and T-tropic viruses, respectively. Taken together, our results define a novel role for Tat in HIV-1 pathogenesis that promotes the infectivity of both M- and T-tropic HIV-1 strains in primary human leukocytes, notably in monocytes/macrophages.
Figures


References
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder C C, Feng Y, Kennedy P E, Murphy P M, Berger E A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1 alpha, MIP-1 beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Barillari G, Gendelman R, Gallo R C, Ensoli B. The Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, a growth factor for AIDS Kaposi sarcoma and cytokine-activated vascular cells, induces adhesion of the same cell types by using integrin receptors recognizing the RGD amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:7941–7945. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhardwaj R, Becher E, Mahnke K, Hartmeyer M, Schwarz T, Scholzen T, Luger T A. Evidence for the differential expression of the functional alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor MC-1 on human monocytes. J Immunol. 1997;158:3378–3384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

