Metabolic labeling of woodchuck hepatitis B virus X protein in naturally infected hepatocytes reveals a bimodal half-life and association with the nuclear framework
- PMID: 9765489
- PMCID: PMC110361
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.11.9359-9364.1998
Metabolic labeling of woodchuck hepatitis B virus X protein in naturally infected hepatocytes reveals a bimodal half-life and association with the nuclear framework
Abstract
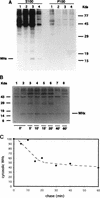
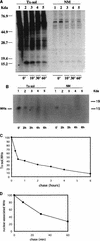
In order to identify potential sites of hepadnavirus X protein action, we have investigated the subcellular distribution and the stability of woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) X protein (WHx) in primary hepatocytes isolated from woodchucks with persistent WHV infection. In vivo cell labeling and cell fractionation studies showed that the majority of WHx is a soluble cytoplasmic protein while a minor part of newly synthesized WHx is associated with a nuclear framework fraction (20%) and with cytoskeletal components (5 to 10%). Pulse-chase experiments revealed that cytoplasmic WHx has a short half-life and decays with bimodal kinetics (approximately 20 min and 3 h). The rates of association and turnover of nucleus-associated WHx suggest that compartmentalization may be responsible for the bimodal turnover observed in the cytoplasm.
Figures

References
-
- Aldrich C E, Coates L, Wu T T, Newbold J, Tennant B C, Summers J, Seeger C, Mason W S. In vitro infection of woodchuck hepatocytes with woodchuck hepatitis virus and ground squirrel hepatitis virus. Virology. 1989;172:247–252. - PubMed
-
- Amellem O, Stokke T, Sandvik J A, Pettersen E O. The retinoblastoma gene product is reversibly dephosphorylated and bound in the nucleus in S and G2 phases during hypoxic stress. Exp Cell Res. 1996;227:106–115. - PubMed
-
- Buendia M A. Hepatitis B viruses and hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv Cancer Res. 1992;59:167–226. - PubMed
-
- Capco D G, Wan K M, Penman S. The nuclear matrix: three-dimensional architecture and protein composition. Cell. 1982;29:847–858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

