Methanococcus jannaschii flap endonuclease: expression, purification, and substrate requirements
- PMID: 9765572
- PMCID: PMC107589
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.20.5406-5412.1998
Methanococcus jannaschii flap endonuclease: expression, purification, and substrate requirements
Abstract
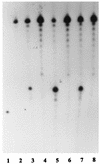
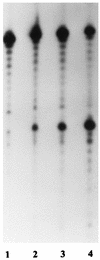
The flap endonuclease (FEN) of the hyperthermophilic archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii was expressed in Escherichia coli and purified to homogeneity. FEN retained activity after preincubation at 95 degrees C+ for 15 min. A pseudo-Y-shaped substrate was formed by hybridization of two partially complementary oligonucleotides. FEN cleaved the strand with the free 5' end adjacent to the single-strand-duplex junction. Deletion of the free 3' end prevented cleavage. Hybridization of a complementary oligonucleotide to the free 3' end moved the cleavage site by 1 to 2 nucleotides. Hybridization of excess complementary oligonucleotide to the free 5' end failed to block cleavage, although this substrate was refractory to cleavage by the 5'-3' exonuclease activity of Taq DNA polymerase. For verification, the free 5' end was replaced by an internally labeled hairpin structure. This structure was a substrate for FEN but became a substrate for Taq DNA polymerase only after exonucleolytic cleavage had destabilized the hairpin. A circular duplex substrate with a 5' single-stranded branch was formed by primer extension of a partially complementary oligonucleotide on virion phiX174. This denaturation-resistant substrate was used to examine the effects of temperature and solution properties, such as pH, salt, and divalent ion concentration on the turnover number of the enzyme.
Figures





References
-
- Bambara R A, Murante R S, Henricksen L A. Enzymes and reactions at the eukaryotic replication fork. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:4647–4650. - PubMed
-
- Bult C J, White O, Olsen G J, Zhou L, Fleischmann R D, et al. Complete genomic sequence of the methanogenic archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii. Science. 1996;273:1058–1073. - PubMed
-
- Ceska T A, Sayers J R, Stier G, Suck D. A helical arch allowing single-stranded DNA to thread through T5 5′-exonuclease. Nature. 1996;382:90–93. - PubMed
-
- DeMott M S, Shen B, Park M S, Bambara R A, Zigman S. Human RAD2 homolog 1 5′- to 3′-exo/endonuclease can efficiently excise a displaced DNA fragment containing a 5′-terminal abasic lesion by endonuclease activity. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:30068–30076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

